Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
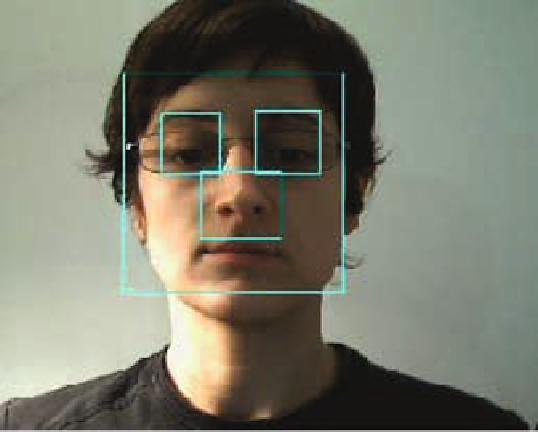
Fig. 4
O
PEN
CV face and local feature detection
Another important innovation was the use of a cascade of classifiers to reduce
the computation time and increase accuracy. First, a two-feature strong classifier is
applied to the integral image. The threshold is set to minimise false negatives at
the cost of a high false positive rate (up to 50%). This rapidly rejects background
regions and focuses attention on more promising regions. Regions which pass the
first classifier are passed to the next classifier in the cascade. The strategy is to reject
negatives as early as possible and gradually reduce the number of false positives as
the regions pass through the cascade. A region that passes through every level of the
cascade is classified as a face.
The Viola-Jones method can be applied to other objects besides faces, but works
best on objects with “blocky” features rather than those where the outline is the most
distinguishing characteristic. This is because the classifier must include part of the
background of an object in its model of the object's outline.
O
PEN
CV includes pre-trained cascades for frontal faces, profile faces, eyes,
noses and mouths. Our implementation used nested cascades within the O
PEN
CV
face detector to find local features (eyes and noses) within detected faces (see fig-
ure 4). Feature extraction is discussed in section 3.3.
The detection of profile views works well when the background is plain but less
well with a textured background, for the reason mentioned above. The detection of
profile faces was improved using skin detection (see below).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search