Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Mode of Action
The diphenyl ether herbicides are active only in the presence of light and
cause chlorosis of leaf tissue. They inhibit the Hill reaction in photosynthesis
and photophosphorylation. However, the primary mode of action probably
involves the photosynthetic reduction to form radicals, which initiate destruc-
tive reactions in lipid membranes leading to cell leakage.
Toxicology
The toxicity of the product is dependent on the formulation. Formula-
tions such as emulsifiable concentrates contain inert additives or solvents
which can severely irritate or damage the skin and eyes. Before handling, read
the label carefully.
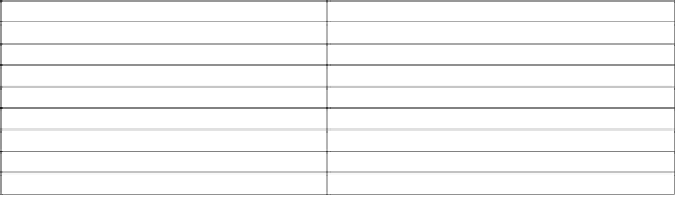
Table 5.17
Commercial products containing diphenyl ether herbicides.
Active Ingredient
Trade Name
Fluoroglycofen-ethyl
Compete
Fomesafen
Flexstar, Reflex
Oxyfluorfen
Goal
Acifluorfen
Blazer
Lactofen
Cobra Herbicide
Nitrofen
Nitrofen, Trizilin
Fluorodifen
Fluorodifen
Bifenox
Modown
l.
Benzothiadiazoles
Mode of Action and Toxicity
The only representative of this group is bentazon. It is used as a selective
postemergence control of many broadleaf weeds. It is usually formulated as a
soluble concentrate of the sodium salt of bentazon.
Its mode of action is similar to other photosynthesis inhibitors in that its
activity is dependent on light. It inhibits photosynthetic carbon dioxide fixa-
tion and photosynthetic electron transport.
Basagran is mildly irritating to eyes and respiratory tract and is therefore
designated to Toxicity Class III.
One of the only commercial product with bentazon as the sole active is
Basagran. Storm is a product that contains aciflurofen along with bentazon.