Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
c.
Amides
Mode of Action
There are no consistent modes of action for this group. They are similar
in activity to the acetanilides. These soil-applied preemergent herbicides have
been reported to inhibit root and shoot elongation but are not trasnslocated in
the xylem.
Modes of action of this group are severalfold. Naptalam interferes with
cell growth and development by affecting auxin transport, while the mode of
action of butam diphenamid is unknown. Propylzamide interferes with cell
division and diflufenican causes chlorosis resulting from inhibition of caro-
tenoid biosynthesis. Carbetamide, naproamide, and propyzamide are thought
to act by inhibiting protein synthesis.
Toxicology
Amids are moderate to mildly irritating. Several formulations may con-
tain solvents which can cause injury by both inhalation and oral ingestion.
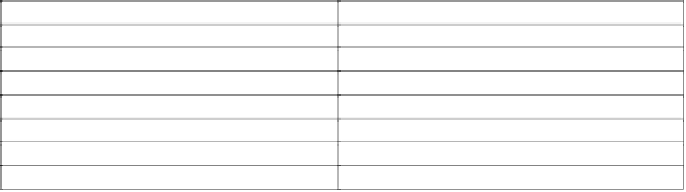
Among the amides are the products listed in
Table 5.11
.
Table 5.11
Commercial products containing amides.
Active Ingredient
Trade Name
Dimethenamide
Frontier
Napropamide
Devrinol, Naproguard
Propanil
Stam, Stampede, Strel
Bensulide
Betasan, Prefar
Naptalam
Alanap-L, Naptro
Propyzamide (pronamide)
Kerb
Carbetamide
Carbetamex
d.
Benzoic or Arylaliphatic Acid Herbicides
Mode of Action
The herbicides resemble and mimic auxins in the activity. They compete
with natural auxins, cause abnormal elongation at the growing terminals, tis-
sue proliferation, induce adventitious roots, and modify the arrangement of
leaves and other organs. These herbicides act in the same way as the chloro-
phenoxy acids (2,4-D and relatives); however, the specific mechanism of ac-
tion of the benzoic acid herbicides is unknown.
Table 5.12
Commercial products containing benzoic or arylaliphatic acid.
Active Ingredient (common name)
Trade Name
Chloramben
Amiben, Vegiben
Dicamba
Banvel, Metambane, Scotts Proturf, Veteran
2,3,6-Trichlorobenozic acid (2,3,6-TBA)
Tribac