Database Reference
In-Depth Information
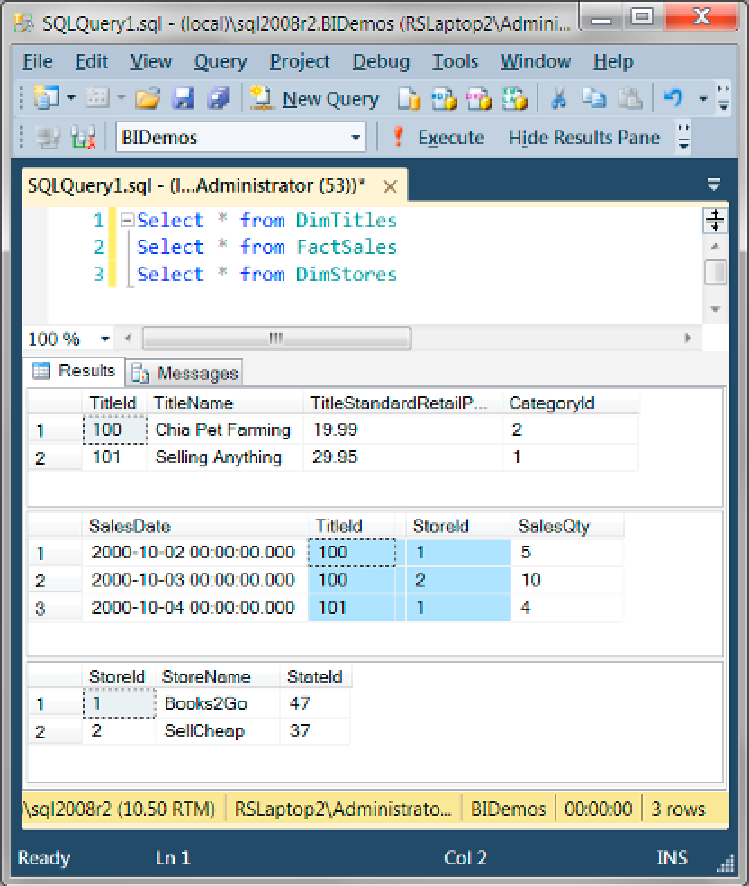
Figure 4-19.
A direct many-to-many dimension
Indirect Many-to-Many Relationships
In an indirect many-to-many relationship, one row is associated with multiple rows of another table. A measured
value in the primary fact table can be associated with one or more rows of data from each of the dimension
tables. For example, one title may have only one author, whereas another has many authors. If a particular book
has two authors, it will always have two authors regardless of the sales event in the fact table with which we are
concerned. Therefore, from the position of a fact table's measures (such as sales quantity), sometimes a quantity
will be associated with one author and other times with many authors!
If we try to track this in a fact table, we will need two rows for each title sold, as shown in Figure
4-20
. Note,
however, that this can lead to a problem known as
double counting
.