Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
1
C−burst
0.5
0
−0.5
A−burst
D−burst
B−burst
−1
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1
Area of
A−burst
Area of
B−burst
0.8
Area of
C−burst
Area of
D−burst
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
0
200
400
600
800
1000
Time (ns)
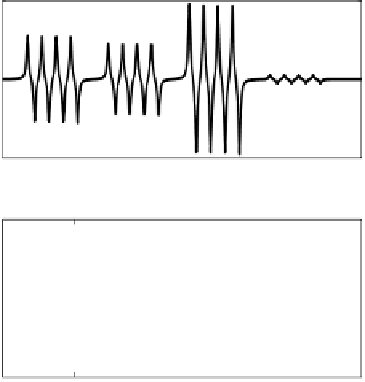
Figure 2.19: Area detector for servo burst demodulation.
in this direction is the digital area detection which samples the burst signals
and adds the absolute values of pre-defined number of samples [164]. The
result of the summation is proportional to the burst area. The burst waveform
is filtered before it is sampled to reduce aliasing effects. Let y
A
(kT
S
)bethe
samples from the A-burst waveform, sampled at intervals of T
S
. Then the area
of this burst is,
N−1
X
A
area
=
|y
A
(kT
S
)|.
(2.20)
k=0
The number of samples (N) is selected such that the summing window is
equal to an integer number of periods of the burst waveform. If the sampling
of the burst is not synchronized with the zero-crossings of the waveform, the
estimated area differs from its true value, and the reliability of the PES becomes
questionable.
Two other methods proposed for estimating amplitude (or area) of a burst
waveform from its samples are digital maximum likelihood detection [216], and
coherent detection with selective harmonics [3]. The estimated burst amplitude
using these two methods are shown below for the samples y
A
(kT
S
).
Digital Maximum Likelihood Detection:
A
ml
=
y
A
d
0
d
0
d
0
.
(2.21)