Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
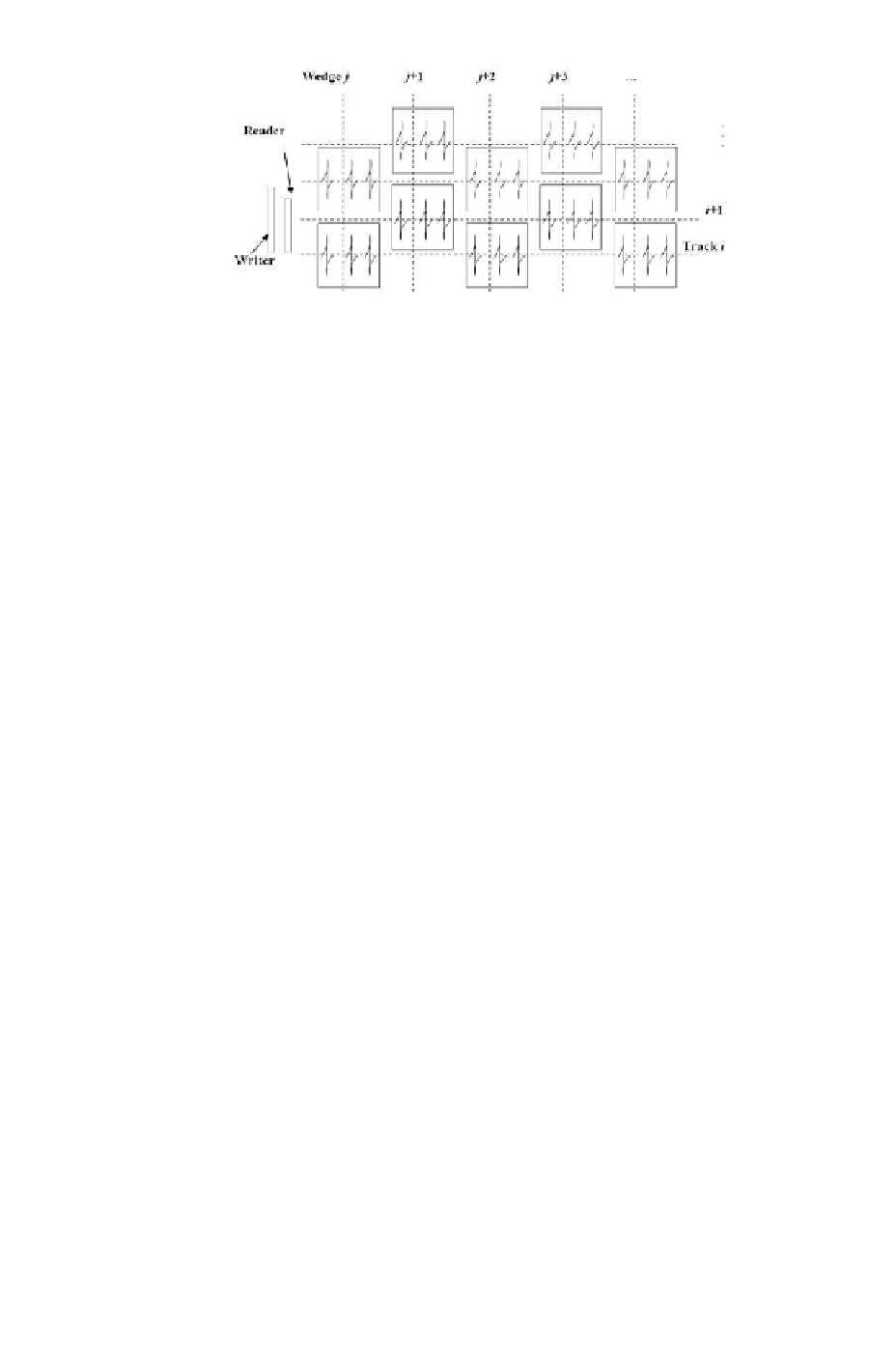
Figure 5.2: Illustration of SSTW process.
In the above mentioned process, the MR head reads previously written
information so that the the actuator's radial position can be controlled and
the servo burst can be written at the next position. Therefore, the geometry
of the read-write head is a crucial factor in the realization of this method.
Its geometry should be such that for any radial position between the ID and
the OD location, the read element can read at least one of the previously
written tracks or timing information with reasonably good signal-to-noise ratio
(SNR) when the write-head writes the next servo pattern or timing pattern or
both. When the j
th
timing mark of the i
th
STW track is scanned by the read
element placed off-track from the center of the track, it is used to determine
the position of the (j+1)
th
timing mark of the (i+1)
th
STW track which muct
be aligned with the (j +1)
th
timing mark of the i
th
STW track. To make this
alignment possible, the error contributed by timing delays from the read and
write electronics, and the physical separation between the read and the write
elements must be precisely measured, calibrated, and controlled. In practice,
the error cannot be reduced to zero. Moreover, the error in one track affects
the position of the timing marks in the following track. If proper measure is
not taken, the error continues to accumulate from the starting track till the
end track. Such clock error propagation and track error prorogation must not
beallowedtogrow.Methodsusedtocontain the propagation of these errors
are explained next.
5.4.2 Track Propagation
Figure 5.3 shows a simpli
fi
ed block-diagram of a SSTW servo loop where C(z)
and P(z) represent the transfer functions of the controller and the plant, re-
spectively. The external signal n(z) represents all torque disturbances, in-
cluding D/A quantization noise, power ampli
fi
er noise, and any torque due to
air-turbulence impinging upon the actuator, suspension and slider. Moreover,
there are disturbances (d(z)) due to non-repeatable disk motions, and PES de-
modulation noise (v(z)) which includes electrical noise and A/D quantization