Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
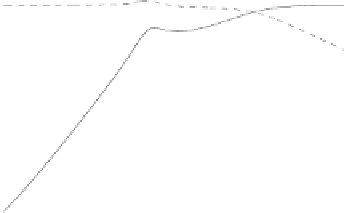
follows the VCM loop. For frequencies above f
V
, the gain of the VCM is below
0-dB where as the microactuator path has a higher gain. The parallel loop
thus crosses the 0-dB line at a -20 dB/dec slope following the microactuator
path. The combined loop has a phase delay of less than 120
◦
following the
microactuator path, giving a phase margin of more than 60
◦
.
2−stage open loop−parallel
80
60
40
20
0
−20
10
2
10
3
10
4
−50
−100
−150
−200
10
2
10
3
10
4
Frequency in Hz
Figure 3.73: Open loop transfer function. Solid line: combined loop, dash-dot
line: VCM path, dashed line: PZT path.
20
0
−20
−40
−60
−80
−100
10
1
10
2
10
3
10
4
10
5
Freq. in Hz
Figure 3.74: S (solid) and T (dashed line) for parallel structure.
Now let the desired crossover frequency of the microactuator loop be f
m
= 2 kHz, and the same for the VCM path be f
V
= 1 kHz. The gain and
phase delay of the microactuator loop at 2 kHz are 1 and 76
◦
, respectively.
The gain and phase of the VCM loop are 0.4133 and −139
◦
, respectively at
2000 Hz. These two loops work in parallel and generate a loop gain of 1.2419