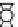Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 6.1 Technical specifications of the fuel cell system
Fuel cell system
Stack output electric power
Max. 2.5 kW, dead-end
Electric power after DC-DC
Max. 2.0 kW
Stack output voltage range
22-34 V
Max 500 W s
-1
Power rate
Cell number
34 cells
Hydrogen
Purity: 99.999 H
2
FCS inlet gas pressure: 500 kPa
FCS inlet gas stream: at least 3 Nm
3
h
-1
Nitrogen
Purity: 99.999 N
2
FCS inlet gas pressure: 500 kPa
FCS inlet gas stream: at least 1 Nm
3
h
-1
Max stack temperature
343 K
Max cooling water
333 K
Air compressor
Side channel, 24VDC, max press. 16 kPa
Hydrogen purge valve
Cut-off valve, normally closed, 24VDC, NPT 1/8''
Cooling water pump
24VDC, 20 kPa, 7 l/min
Humidification water pump
24VDC, 500 kPa, 0.17 l/min
CONDENSER
V1
V2
Purge valve
P
STACK
Water collection tank
V1
V2
F
Heat
Exchanger
T
T
N
2
H
2
AIR IN
V2
AIR OUT
Water collection tank
F
P
COMPRESSOR
V1 = ON/OFF Valve
V2 = Flow rate regulation valve
P = pressure sensor
F = flow rate sensor
I = current sensor
V = voltage sensor
T = temperature sensor
I
V2
V1
V
+
-
DRECHSEL
ELECTRIC LOAD
AIR
Fig. 6.1
Scheme of the fuel cell system experimental apparatus and location of the sensors
cell voltages. National Instruments FieldPoint units are used to acquire all the
voltage signals generated by the sensors and to control the overall system. The
system is also provided with a small lead-acid battery of 24 V and 6 Ah for
the start-up operation of the system, when the energy supplied by the stack is lower
than the electric request by the auxiliaries.