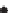Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
200
Flagstaff
100
D
E
A
0
200
Portland
100
D
S
E
A
0
JFMAMJ
Month
JASOND
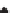
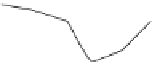
Fig. 10.6
Water balance for MTC site and for bimodal winter rain and summer rain
climate in Arizona. Actual evapotranspiration (
E
A
, dense stippling), precipitation (solid
diamonds) and potential evapotranspiration (open diamonds) contribute to water deficit (D).
S, winter surplus. (From Stephenson 1990.)
equivalent to that in the MTC of Portland, Oregon (
Fig. 10.6
). Under summer-
rain conditions, when evapotranspiration rates are substantial, plants on severe
sites may actually be exposed to summer-drought conditions and unable to fully
utilize this summer moisture input (Vankat
1989
). A similar phenomenon is
observed in the eastern Cape region of South Africa where MTV similar to the
Cape fynbos is distributed under a climatic regime of even rainfall throughout
the year, but due to high summer evapotranspiration it exists under essentially
a winter-rainfall climate (van Wilgen
1984
).
On any given landscape soil moisture stress can vary markedly dependent on
microsite characteristics. Plants distributed on exposed rocky ridgelines or equator-
facing slopes with shallow soils may experience soil drought stress when other
parts of the landscape are less stressed, and plants sort out along such gradients.
Thus, landscapes comprise a mosaic of plants tolerant of varying degrees of
drought stress and with different strategies for coping with water stress (e.g.
Mooney
1989
; Mahall
et al.
2010
). Climatic seasonality plays a key role in