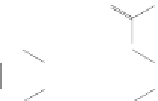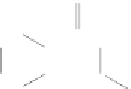Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
corals), echinodermata (e.g., sea urchins), tunicates (e.g., sea squirts), bryozoa and
bacteria [52]. The secondary metabolites include: acetogenins, alkaloids, amino acids,
fatty acids, heterocyclics (furans, lactones), polyphenolics, steroids and terpenoids
[2]. These compounds exhibit anti-bacterial, anti-fungal and anti-oxidant activities.
A number of different anti-fouling compounds targeting different groups of
microorganisms and macroorganisms are produced by some marine bacteria.
These bacteria are a promising source of environmentally friendly anti-fouling agents.
Only a limited number of marine bacteria have been screened so far for anti-fouling
activities. The main reasons for this are the non-cultivability of marine bacterial
strains, their complexity and the resource intensive nature of these studies [75].
O
OH
OH
N
N
N
N
Phenazine-1-carboxylic acid
1-Hydroxyphenazine
O
O
N
H
N
H
C
7
H
15
C
9
H
10
2-
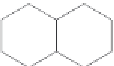
N
-heptylquinol-4-one
2-
N
-nonylquinol-4-one
O
O
O
O
OH
O
HO
OH
OH
OH
Pyolipic acid
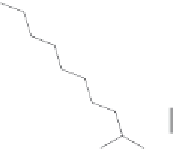
Figure 2.17
Metabolites with anti-fouling activity isolated from a culture of the
nudibranch-associated
Pseudomonas sp
., NUDMB50-11