Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Rhizobacteria
Pathogen
Other
signals
LPS
Flagellin
AVR
gene product
R
gene product
Plant receptors
HR
JA
Systemically
transported
SAR signal
ET
SA
Systemically
transported ISR signal
NPR1
NPR1
modulating
signal
NPR1
modulating
signal
TGA
transcription
factors
NPR1
NPR1
SNI
Transcriptional activation
Transcriptional activation
Defensive compounds
PRs, defensive compounds
ISR
SAR
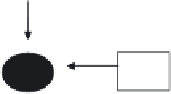
Figure 4.1
A model for the signal transduction network controlling induced systemic resistance (ISR)
mediated by plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and pathogen-induced systemic acquired resistance
(SAR) in
Arabidopsis thaliana.
LPS = lipopolysaccharide; PRs = pathogenesis-related proteins;
AVR
= avirulence gene product;
R
= resistance gene product; HR = hypersensitive response; SA = salicylic
acid; JA = jasmonic acid; ET = ethylene; NPR1 = a regulatory protein involved in signalling in SAR and
ISR in
A. thaliana;
SNI = transcriptional repressor of SAR genes; TGA transcription factors = family of
transcription factors interacting with SA-induced NPR1. (From Walters & Heil (2007), with permission
from Elsevier.)
induction, the role of these
PR
genes in the expression of resistance is unclear (Durrant &
Dong, 2004) and induction of resistance is not always accompanied by expression of
PR-1
(Sparla
et al.,
2004).
In contrast to SAR, ISR develops as a result of colonisation of plant roots by certain
strains of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) and is mediated by a jasmonic