Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
50
Pumped Hydro Generation
45
40
Other
Pumped Hydro
Pumping
35
30
Coal
25
20
Gas
15
10
Nuclear
5
0
00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
Time (hours)
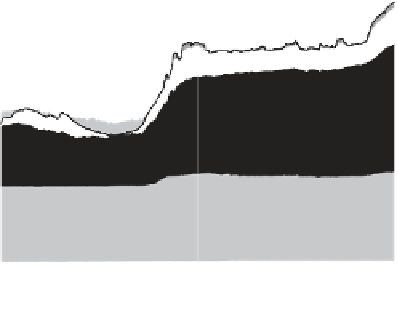
Figure 3.7
Demand curve of the England and Wales power system (Source: National Grid plc)
The reader should not misunderstand the nature of the layering in Figure 3.7. For example,
it would be wrong to assume that a constant load like offi ce lighting is supplied from a nuclear
power station while a toaster is supplied from coal! Rather a power system could be likened
to a bathtub in which water is fed from all the generators and is extracted by loads. The level
of water in the bathtub would represent the frequency of the system which the operators
endeavour to keep constant. Some generators, e.g. nuclear, provide a constant infl ow of water.
Other generators are instructed to supply water when the level is detected to be falling. In
such an analogy there is no way someone can tell which 'generated water molecule' reaches
which load. In other words, electrons cannot be labelled.
3.4.2 Demand Forecasting
Accurate forecasts of demand are required because:
•
Electrical energy cannot yet be stored economically.
•
The largest proportion of generating plant is thermal in nature. An unfortunate feature of
this plant is the considerable delays involved in preparing the cold generators for connec-
tion to the power system (several hours) and the restrictions in the rate at which a steam
driven turbogenerator can be loaded after connection. These operational delays are dictated
by the thermal/mechanical safety requirements of massive boilers and of turbogenerator
sets.
•
Thermal generators using steam turbines have an upper limit of power generation equal to
their
nameplate rating
, but also a lower limit dictated by cavitation problems in the turbine
blades at low throughputs of steam. Consequently, when a turbogenerator is connected to
the network it should be loaded to a level at least equal to the minimum recommended by
the manufacturers (from 30 to 50% of rated power).