Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Electricity distribution and renewable energy
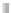
Accrued price,
cents ECU
Large thermal plant
4.0
HV Transmission
RE fed in at lower voltage
than thermal plant
Value is therefore higher
4.6
132 kV distribution
4.8
Industry
33/11 kV distribution
Commerce (8.6)
Domestic (9.9)
Prices are average levels in cents ECU/kWh, and are approximate
Figure 7.10
Principles behind embedded generation benefi ts.
tariffs, and with other case studies in Europe and the United States. The analysis
enabled average levels of electricity price to be established at key points in the distribution
chain:
•
at the busbars of large thermal plant;
•
at exit from the high voltage transmission system;
•
at delivery to the consumer.
Conventional terminology delineates three stages of electricity supply:
•
generation;
•
high voltage transmission (often abbreviated to ' transmission ' );
•
distribution.
For each of these stages in the supply chain, costs can be allocated under four headings:
•
fuel
(fuel cost purchases for generators and power losses in transmission and distribution);
•
operating
, refl ecting all operating costs including overheads;
•
depreciation
of capital assets;
•
profi t
on a historic cost basis.