Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
4
Generation cost,
€
/MWh
4
Generation cost,
€
/MWh
O&M
Fuel
Capital
O&M
Fuel
Capital
30
30
20
20
10
10
0
0
Gas
Wind
Gas
Wind
20 year life, 5% discount rate
12 year life, 12% discount rate
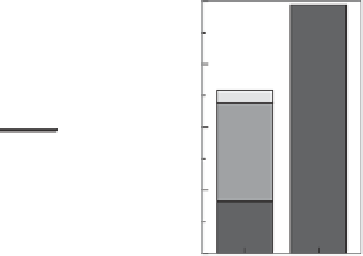
Figure 7.1
Generation costs as a function of fi nancing terms. (Courtesy of David Milborrow)
Table 7.2 shows that the fi nancing terms can have a very signifi cant impact on the capital
cost element of electricity generating costs. The most stringent criteria with the highest inter-
est rate of 12% mean that annual charges will be double those associated with more relaxed
criteria with the lowest interest rate shown at 5%. If the capital cost element of the total
generation cost is small, e.g. as in the case of gas-fi red generation, changes in the fi nancing
terms will have very little impact on generating costs. In the case of renewable energy tech-
nologies such as wind, wave, photovoltaics and tidal, where capital costs form the largest
element of generation cost, the impact will be much greater.
Figure 7.1 illustrates this point, comparing generation costs for gas and wind, fi rst with the
fi nancial criteria in the top row of Table 7.2 and second with the criteria in the bottom row.
The results clearly illustrate the effect of moving from public to private sector fi nancing. The
prices move upwards, but the effect on a capital-intensive generation source, such as wind,
is much more pronounced. The data on installed costs and performance levels were drawn
from the Danish Energy Agency [1] .
Only wind and gas are compared in Figure 7.1 whereas the IEA data [2] shown in Figure
7.2 cover a much wider range of renewable energy technologies. Again, the relative viability
of the different sources is highly dependent on the fi nancial criteria.
The IEA data do not include wave energy, currently the subject of increasing research
activity in the UK and elsewhere, but commercial costs are inevitably very uncertain. The
wave energy community suggests that a near-term generation cost target is around $80/MW h
(
60/MW h).
€
7.3 Economic Optimization in Power Systems
7.3.1 Variety of Generators in a Power System
Power systems are in general fed by a variety of generators using a range of fuels. Each
generator type has its own characteristics and is suited for a particular function within the
system. Table 7.3 summarizes these characteristics and extends the features covered in Table
2.4 of Chapter 2 .