Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
5. Conserve water in the root zone by reducing losses due to runoff and
evaporation
6. Adopt improved irrigation/fertilization techniques that deliver water and
nutrients directly to plant roots at the most critical stage of plant growth
7. Use improved/genetically modified (GM) plants/cultivars that are efficient
in resource utilization and are adapted to current and future biotic and
abiotic stresses
8. Synchronize crop requirements (rooting depth, pH, water and nutrient
needs) with soil properties through use of soil survey data and land use
capability classification
9. Minimize losses by adopting soil-specific management that increases
productivity
10. Adopt techniques of soil/crop management that increase productivity per
unit area of land, time, and input (energy, nutrients, and water)
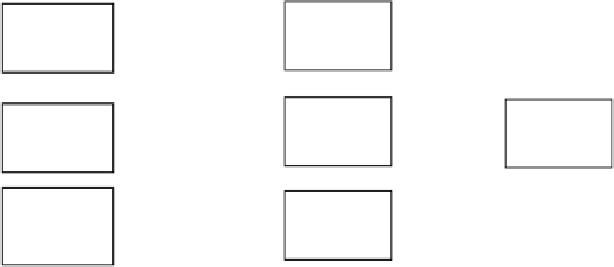
Basic principles of management and conservation of soil are outlined in
Figure 18.1. The strategy is to adopt recommended management practices (RMPs)
that increase soil organic matter (SOM), improve soil structure, and strengthen
elemental cycling. Adoption of RMPs would decrease losses of water and nutri-
ents out of the ecosystem, reverse degradative trends, and restore degraded/deser-
tified soils.
Management and
Conservation of Soil
Increasing
soil organic
matter pool
Improving soil
structure
Strengthening
elemental cycling
No-Till farming
Improving
bioturbation
Complex
rotations
Decreasing soil
disturbance
Recycling
biosolids
Cover cropping
Manuring and
integrated
nutrient
management
Enhancing
ground cover
Agroforestry
system
Decreasing Losses From the Ecosystem
fIguRe 18.1
Processes and practices of enhancing soil quality.