Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
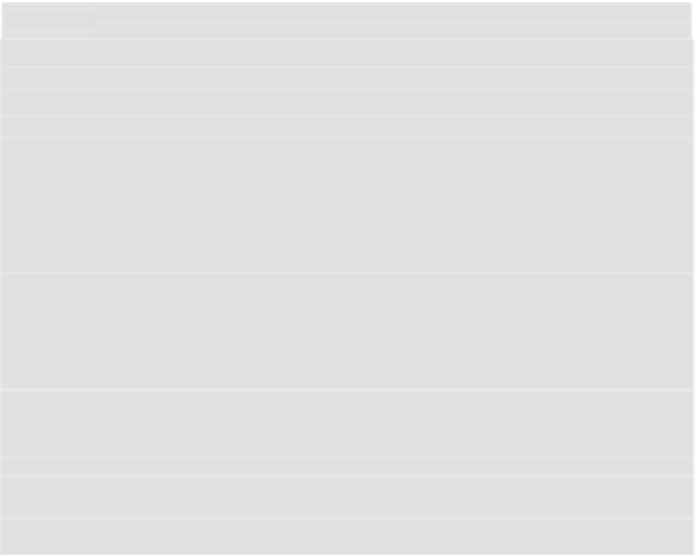
Table 1.1
A scale of a judgment matrix definition
Evaluation of
importance
Qualitative evaluation
Note
Identical importance
By the given criterion, projects
have an identical rank
1
Weak superiority
Reasons on preference of a project over the other one are flimsy
3
Strong (or essential) superiority
There are relevant proof of the essential superiority of one of the
projects
5
Obvious superiority
There are convincing demonstrations in favour of one of the projects
7
Absolute superiority of one of the
projects over the other is extremely
evident
Preference of one of the projects is well-founded
9
Intermediate values between the
adjacent evaluations
Used when the compromise is necessary
2. 4. 6. 8
Then
λ
=
−
0
362
;
λ
=
−
0
140
+
1
305
i
;
1
2
λ
=
−
0
140
−
1
305
i
;
λ
=
4
390
.
3
4
Let us find an eigenvector for maximum eigenvalue
λ
=
4
390
ɦɚɤɫ
§
1
−
4
390
5
6
7
·
¨
¸
1
§
ω
·
¨
¸
1
−
4
390
4
6
¨
1
¸
5
¨
¸
ω
¨
¸
1
1
2
=
0
¨
¸
¨
¸
1
−
4
390
4
ω
¨
¸
¨
¨
¸
¸
6
4
3
¨
¸
ω
1
1
1
©
¹
1
−
4
390
4
¨
¸
©
7
6
4
¹
On multiplying the matrixes, we obtain the following set of equations
-
−
3
390
ω
+
5
ω
+
6
ω
+
7
ω
=
0
1
2
3
4
°
°
®
0
200
ω
−
3
390
ω
+
4
ω
+
6
ω
=
0
1
2
3
4
0
166
ω
+
0
250
ω
−
3
390
ω
+
4
ω
=
0
°
¯
1
2
3
4
°
0
142
ω
+
0
166
ω
+
0
250
ω
−
3
390
ω
=
0
1
2
3
4
which only has a trivial solution.
Let us substitute any of equations of the system with the equation
, as a result
ω
+
ω
+
ω
+
ω
=
1
1
2
3
4
ω
=
0
101
ω
=
0
045
we'll obtain a solution:
.
If it is necessary to select a project with the greatest public importance among four projects, the fuzzy set
is to be considered
ω
=
0
619
;
ω
=
0
235
;
;
3
4
1
2
{
}
0
Then project No. 1 is to be selected because it has the greatest grade of membership to the constructed
fuzzy set.
619
/
ʋ
0
235
/
ʋ
2
0
101
/
ʋ
3
0
045
/
ʋ
4
.
In [71—72] values of membership functions of fuzzy set are defined by an
expert group following the rank orderings of objects.
Model-building methods of semantic spaces unlike building methods of
separate fuzzy sets are sparse. It is necessary to outline a model-building
techniques of linguistic terms of frequency evaluations developed by
D.A.Pospelov, I.V.Ezhkova [73—74]. A method shortage is lack of formal
algorithm of membership functions building for terms. Ambiguity of building
process and of its quality dependence on experience and skills of contributors are
consequences of that shortage. The method [73—74] was further developed in
methods of S.G. Svarovsky [75] and I.A.Khodashinsky [76].