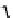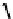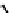Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Three variables were considered:
Z
— distance between value of characteristic
X
of
n
-th software product, and value of characteristic of the reference pattern
of software products;
Z
— distance between value of characteristic
X
of
n
-th
software product, and value of characteristic
X
of the reference pattern of
Z
— distance from value of characteristic
X
of
n
-th
software products;
X
of the reference pattern of
software product,
n
=
1
12
to value of characteristic
software products.
Each variable accepts three linguistic values "low", "mean", "high", to which
values 0, 1 and 2 are put in correspondence withy the aim to construct logic
function.
Nu
merical values of variables
Z
were denoted with
n
Z
1
,
n
Z
2
,
Z
,
Z
,
Z
3
,
n
n
=
1
12
, accordingly:
(
)
(
)
2
2
n
n
n
Z
=
B
−
A
+
B
−
A
,
n
=
1
12
;
1
11
11
12
12
(
)
(
)
2
2
n
n
n
Z
=
B
−
A
+
B
−
A
,
n
=
1
12
;
2
21
21
22
22
(
)
(
)
2
2
n
n
n
Z
=
B
−
A
+
B
−
A
,
n
=
1
12
.
The interval [0; 0.3] is put in correspondence to linguistic value "low" of variables
Z
,
3
31
31
32
32
Z
; [0.3; 0.95] — to value "mean", and interval [0.95;
Z
,
2 ] — to value
"high".
On agreeing with experts, the logic function
F
depending on variables
Z
,
Z
,
Z
began to take three values: “the software product is conditionally transferred to
the next stage and updated routinely”, “an expert is invited to update the software
program”, “a group of experts is invited to update the software program”. Values
0, 1 and 2 were put in correspondence to these values.
The functional model of development of managerial instructions based on the
rating points is given in Fig. 6.2.
Experts formulated the following entry conditions
(
)
F
Z
=
2
=
2
,
1
(
)
(
)
ZF
, and fuzzy conditions "slightly-increase" for
behavior of function by each argument. These conditions were formalized by
means of fuzzy relations, with the related matrixes summarized in Table 6.9.
As a result of formalization of function behavior conditions and entry
conditions [230], the following matrixes of the fuzzy relations with related
elements summarized in Table 6.10, were obtained.
At the cross-section of a line
=
2
=
2
F
Z
=
2
=
2
,
2
3
+
j
of the matrixes
(Table 6.10) there are the values of confidence degrees saying that functio
n
F
will
tak
e value
and a column
1
i
+
1
j
with value of arguments
Z
, equal to
i
,
i
=
0
2
Z
,
Z
,
,
j
=
0
2
, accordingly.