Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Weight and noise estimat error for sampling from N(5, 1)
3
LMS weight
RLS weight
LMS noise
RLSLMS noise
RLS noise
6
2.5
5
2
4
1.5
3
1
2
1
0.5
0
0
0
10
20
30
40
50
Observations
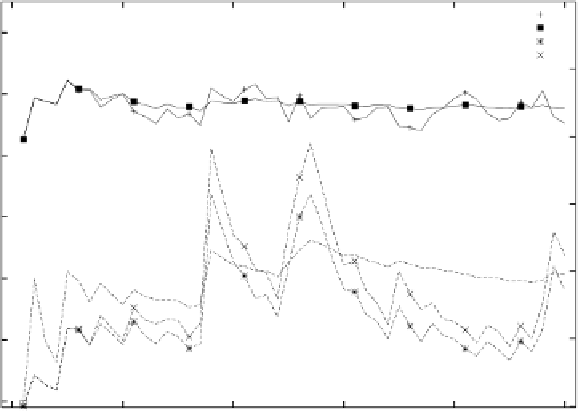
Fig. 5.1.
The graph shows the weight estimate (on the left scale) and noise variance
estimate (on the right scale) of different averaging classifiers when being presented with
observations sampled from
N
(5
,
1). The weight estimate of the RLSLMS classifier is
not shown, as it is equivalent to the estimate of the RLS classifier.
need to be defined. The target function of the second experiment is the sinusoid
f
2
(
x
n
)=sin(
i
n
) with inputs
x
n
=(1
,i
n
), hence, using classifiers that model
straight lines. The experiment is split into two parts, where in the first part, the
function is modelled over the domain
i
n
∈
[0
,π/
2), and in the second part over
i
n
∈
[
pi/
2
,π
). The classifiers are trained incrementally, by presenting them with
observations that are uniformly sampled from the target function's domain.
Statistical significance of difference in the classifiers' performances of estima-
ting the weight vector and noise variance is evaluated by comparing the sequence
of model MSEs and squared noise variance estimation errors respectively, after
each additional observations, and over 20 experimental runs. These sequences
violate the standard analysis of variances (ANOVA) assumption of homogeneity
of covariances, and thus the randomised ANOVA procedure [184], specifically
designed for such cases, was used. It is based on estimating the sampling distri-
bution of the null hypothesis (“all methods feature the same performance”) by
sampling the standard two-way ANOVA F-values from randomly reshued per-
formance curves between the methods, where we use a samples size of 5000. The
two factors are the type of classifier that is used, and the number of observations
that the classifier has been trained on, where performance is measured by the
model or noise variance error. Significant differences are only reported between
classifier types, and Tukey's HSD post hoc test is employed to determine the
direction of the effect.





















Search WWH ::

Custom Search