Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
A
PPM1
PPM2
PA L
PPL1
PPM3
PPL2
VUM
B
C
PPM1
PPM2
PPL1
PPM3
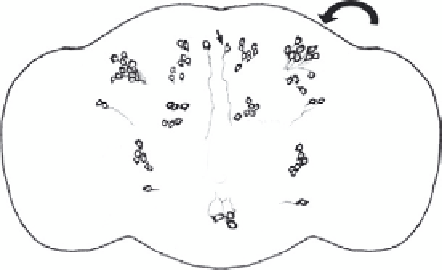
Figure 1.1. (A) Schematic representation of the distribution of dopaminergic neurons in the
Drosophila adult brain. Dopaminergic neurons are grouped in small clusters arranged
with bilateral symmetry. PPM, protocerebral posterior medial; PPL, protocerebral pos-
terior lateral; PAL, protocerebral anterior lateral; VUM, ventral unpaired medial.
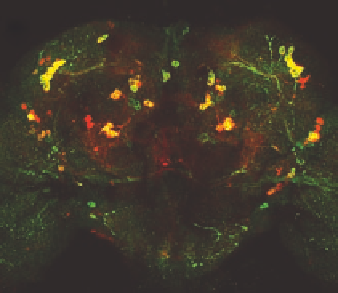
(B) Confocal micrograph revealing the dopaminergic neurons in the adult drosophila
brain. Expression of a GFP reporter (green) is induced by the endogenous tyrosine
hydroxylase promoter and counter-stained with anti-tyrosine hydroxylase antiserum
(red) demonstrating significant but not complete overlap. (C) Detail of a projected
Z
-series of posterior clusters. Axons are revealed as punctate staining with anti-tyrosine
hydroxylase antiserum.
previous work indicates that many fundamental cellular and molecular biological
features of neuronal development and function are conserved between verte-
brates and invertebrates (Ashburner and Novitski, 1976). Recent work indicates
that this conservation makes Drosophila a powerful system for cell biological
studies of neuronal dysfunction.
During embryonic and larval brain development, DA is found to be
expressed in approximately 80 cells in the central nervous system (Budnik and
White, 1988; Lundell and Hirsh, 1994). Many of these cells are grouped together