Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
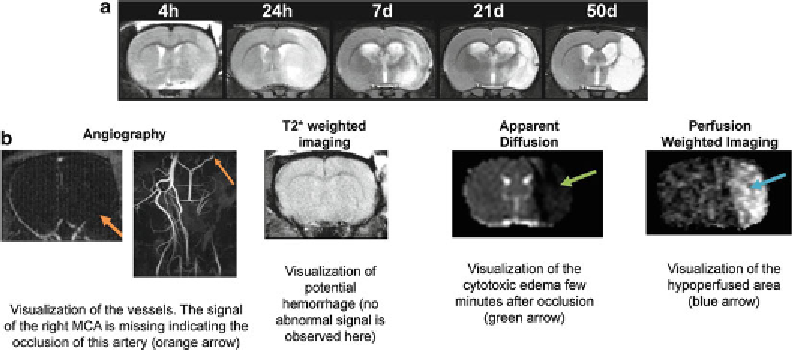
Fig. 3
MRI as a tool of choice for the evaluation of ischemic lesion. (
a
) Longitudinal evolution of the ischemic
lesion in a rat subjected to 90 min of intraluminal transient MCAO. T2 weighted imaging shows clearly the
vasogenic oedema at 24 h post-occlusion and the cystic cavity at latter stages. (
b
) Multiparametric evaluation
of the ischemic lesion using MRI
3.3 Post-mortem
Histology
1. Animals are sacrificed by decapitation following overdose of
anesthesia (deep isoflurane anesthesia).
2. The brain is removed from the skull and quickly frozen by
rapid immersion in isopentane or liquid nitrogen (few sec-
onds). Store it at −80°C until sectioning.
3.3.1 Histological
Staining Which Does Not
Required Post- fi xation
Prepare 4% paraformaldehyde in 0.1 M PB solution as described in
Note 6.
3.3.2 Histological
or Immunohistological
Procedures Requiring
Intracardiac Perfusion
and Fixation
Use a perfusion pump, either a peristaltic pump or a homemade
system made with air bottle connected to mercury column with
tubes (see Note 7).
Wear protective eye goggles, respirator mask, and appropriate
gloves during the whole perfusion process. Perform the procedure
under the hood.
Intracardiac Perfusion
1. Set up perfusion pump; attach perfusion set and perfusion can-
nula (use the appropriate gauge size, 16-24 G, corresponding
to the aorta). Have on hands the 4% paraformaldeyde in 0.1 M
Phosphate Buffer, pH 7.4 and the heparinized saline solution
(10 UI heparin/mL saline) in separate bottles and at room
temperature or a little bit more (no more than 37°C).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search