Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
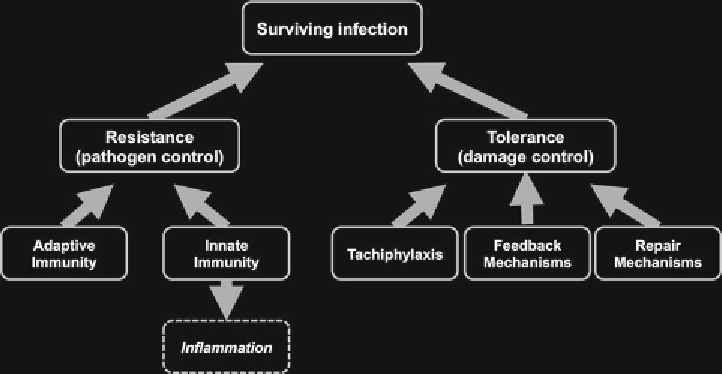
Fig. 1
Surviving infections is achieved either by killing pathogens, or controlling their growth, through adaptive
or innate immunity. TNF, IFNg, IL-1 have a key role in innate immunity but also cause tissue damage. Tolerance,
the ability to control damage induced by pathogens though tachiphylaxis or various protective mechanisms, is
also essential. Tolerance also protects/repair from tissue damage caused by innate immunity/inflammation.
Tissue-protective cytokines are important as a means of regulating inflammation and promoting repair. These
protective cytokines and mechanisms are probably not only important in infections but also when tissue injury
is induced, for instance, by ischemia or trauma
TNF receptors) are now top-selling biologicals in the therapy of
chronic inflammatory diseases. These findings also led to the expan-
sion of the list of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which now include,
among many others, IL-6, IL-18, and IL-33. These cytokines are
essential mediators in host defense against pathogens, and the role of
IL-1 or TNF in innate immunity and of IL-2 or IL-6 in adaptive
immunity are described in any textbook of immunology.
Looking at the right side of Fig.
1
, other cytokines act, among
other things, as negative regulators of inflammatory cytokines, to
control excessive injury due to inflammatory cells. For instance,
IL-10 can be considered as part of the feedback mechanism to
regulate TNF production.
The finding that EPO has tissue-protective activities, originally
identified by Brines et al. in models of ischemic or traumatic brain
injury (
6
), was the most recent addition to the picture of the bio-
logical role of cytokines, and provided a first example of how a
cytokine can be a mediator of “damage control.” Probably, EPO
does so not only by taming inflammation (
7
) but also promoting
repair by various mechanisms that include angiogenesis, neurogen-
esis, and plasticity (
8
).
Induction of EPO expression by hypoxia and ischemia could
well be viewed in this perspective. Transcription of EPO is regu-
lated by HIF-1 while several cytokines implicated in inflammation
and innate immunity are regulated through NF-kB. NF-kB and
Search WWH ::

Custom Search