Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
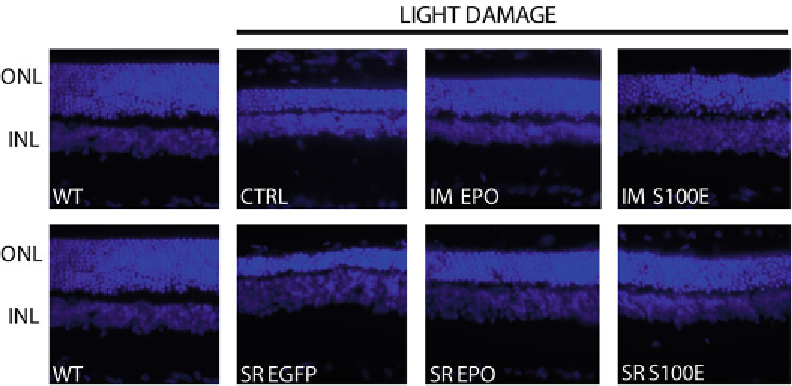
Fig. 6
AAV-mediated delivery of EPO and S100E sustains PR survival in light-damaged rats. The figure shows
the representative retinal histology of Lewis rats whether light-damaged or not.
CTRL
uninjected animals,
IM
intramuscular AAV injection,
INL
inner nuclear layer,
ONL
outer nuclear layer,
SR
subretinal AAV injection,
WT
wild type, age-matched non-damaged Lewis rats. The picture magnification is 40×. Retinal sections were
stained with DAPI to count the rows of PR nuclei in the ONL (
46
). Reproduced from Colella P. 2011 (
46
) by
permission of Oxford University Press
4. Identify the outer nuclear layer (ONL) that contains the
photoreceptor nuclei.
5. Count the number of rows of photoreceptor nuclei that are
present in the ONL in each selected section at 40× magni fication.
Count the rows in two different locations on each side of the
ONH: i.e., the nasal and central on one side, the temporal and
central on the other side (see Notes 48 and 49).
6. Average the number of rows of PR nuclei counted in each eye
and compare PR survival between treated and untreated rats.
Figure
6
shows representative retinal sections taken from treated
and untreated rats (
46
).
4
Notes
1. The pAAV2.1-CMV-EGFP3 plasmid contains the 5¢ ITR from
the AAV serotype 2, the Cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter, the
SV40 intron, the CDS of the enhanced green fluorescent pro-
tein (EGFP), the bovine growth hormone polyadenylation
signal (bGH polyA) and the 3¢ ITR from the AAV serotype 2.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search