Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
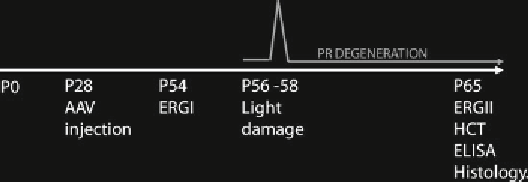
Fig. 4
Schematic representation of the light damage protocol. Setup of the light
damage experiment: (1) Lewis rats are injected systemically or subretinally with
AAV vectors at postnatal day (P) 28; (2) the rats are reared under physiological 12 h
light/dark cycle for 4 weeks; (3) ERGs are recorded before light damage to evaluate
retinal function in treated and untreated eyes; (4) the rats are submitted to light
damage for 48 h; (5) the rats are reared for 7 days under physiological 12 h light/
dark cycle for photoreceptor degeneration to occur; (6) ERGs are recorded at P65
to evaluate the protection from light damage; (7) the rats are sacrificed and hema-
tocrit variations, EPO and S100E expression levels, and PR survival are assessed.
The
gray line
represents the acute damage induced by light that causes photore-
ceptor (PR) degeneration
3.4 Setup of the
Light-Damage Model
of Induced Retinal
Degeneration in Albino
Rats
1. Following AAV injection (see Subheading
3.3
) rear the rats in
a physiological 12 h light/dark cycle for 4 weeks (Fig.
4
).
2. At around postnatal day (P) 56 put the rats separately (1 rat/
cage, 4 total rats-cages/light damage cycle) in clear Plexiglas
cages and insert the cages in the light damage apparatus
(see Notes 8-10, 26).
3. House the rats under continuous light exposure for 48 h
(see Notes 27 and 28) (Fig.
4
).
4. After light damage put the rats back under a physiological 12 h
light-dark cycle for 1 week.
5. Assess retinal function by electrophysiological analyses; then,
sacrifice the rats to collect biological samples for further analysis
including assessing AAV-mediated gene expression and perform-
ing histological analyses (see Subheadings
3.5
-
3.8
) (Fig.
4
).
1. Adapt the rat to the dark by placing it in a darkened ventilated
box for at least 3 h.
2. Perform all the following steps under dim red light.
3. Anesthetize the rat (see Subheading
3.3.2
, step 1).
4. Lay the rat on its stomach on a sterotaxic support with a heat-
ing pad (37.5°C) to maintain it warm during the recordings.
5. Secure the rat using an adhesive gauze.
6. Insert two inactive reference needle electrodes subcutaneously
at the center of the scalp.
7. Insert the ground needle electrode subcutaneously in the tail.
3.5 Evaluation
of Retinal Function
by Full-Field
Electroretinogram
Recordings See Note 29
Search WWH ::

Custom Search