Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
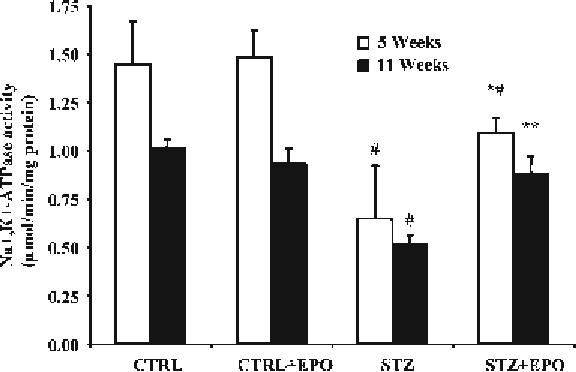
Fig. 5
EPO prevents and restores changes in Na
+
, K
+
-ATPase activity in diabetic
rats. Groups names as in Fig.
2
. Data are mean ± SEM. *
P
< 0.05 vs. STZ, #
P
< 0.01 vs. CTRL and CTRL + EPO
For Na
+
, K
+
-ATPase activity tibial stumps (from the two sciatic
nerves) were de-sheathed at death and homogenized in chilled
solution of 10 mL Tris-sucrose buffer at 1:20 (w/v) in a
glass-glass Potter homogenizer and stored at −80°C for ATPase
determinations. Na
+
, K
+
-ATPase activity was determined spec-
trophotometrically as previously described (
37
).
Diabetes greatly reduced in sciatic nerve Na
+
, K
+
-ATPase activ-
ity by about 60%. The Na
+
, K
+
-ATPase activity in diabetic rats
treated with EPO prevention schedule for 5 weeks was only 22%
different from control rats (Fig.
5
). The change in diabetic rats
treated with EPO according to the therapeutic schedules for 5
weeks was only 16% reduced in respect to control rats.
3.3 Na
+
, K
+
-ATPase
Activity
3.4 Skin Biopsy and
IENF Quantifi cation
This protocol starts at indicated times, namely 6 and 11 weeks
following diabetes induction in rats (see Note 7) for preventive
and therapeutic schedule, respectively, and lasts 5 days.
1. Day 1. Hind paws were collected at sacrifice. Animals were
anesthetized using xylazine-ketamine and sacrificed by means
of exsanguination. After separating plantar glabrous skin
underlines metatarsal bone, punch biopsies (3 mm) under ster-
ile conditions were taken and immediately fixed by immersion
in 1 mL of 2% PLP for 24 h at 4°C.
2. Day 2. Rinse the biopsies in PB twice for 10 min each
(2 × 10 min). Put biopsies in the cryoprotective solution over-
night at 4°C.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search