Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
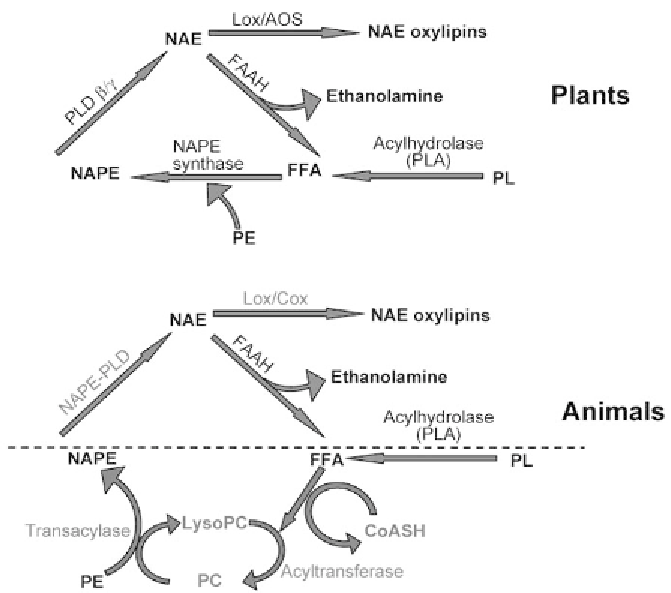
Fig. 14.2.
Schematic comparison of NAE metabolism in plants and animals. NAEs are me-
tabolized to NAE oxylipins (by lipoxygenase,
LOX
),orarehydrolyzedtofreefattyacids
(
FFAs
) and ethanolamine (by fatty acid amide hydrolase,
FAAH
)inbothplantandani-
mal systems. FFAs are incorporated into
N
-acylphosphatidylethanolamine (
NAPE
)directly
by an NAPE synthase enzyme in plants, or by coordinated acyltransferase-transacylase
reactions in animal systems. FFAs can be derived by FAAH-mediated NAE hydrolysis or
from phospholipid acylhydrolases (
PLA
). NAPE is hydrolyzed by a phosphodiesterase ac-
tivity to yield NAEs in both animal and plant systems. In plants, NAE formation is by an
HKD/phosphatidyltransferase (PLD
β
γ
isoforms, where
PLD
is phospholipase D),
whereas in animals NAE formation is by a specific NAPE-PLD zinc-metallohydrolase.
PC
phosphatidylcholine,
CoASH
coenzyme A,
PE
phosphatidylethanolamine,
AOS
allene oxide
synthase,
COX
cylooxygenase. For clarity not all metabolites are shown
or PLD
areflectionofthe
N
-acyl composition of the NAPE precursor (Chapman
2000). Previous work demonstrated that two recombinant
Arabidopsis
PLD
isoforms, PLD
β
γ
, were capable of hydrolyzing NAPE to NAE in
vitro (Pappan et al. 1998). Five PLD isoforms (encoded by 12 genes) have
been identified in
Arabidopsis
(Wang 2004). The most studied and most
highly expressed PLD isoform in plants, PLD
and PLD
α
, did not hydrolyze NAPE in
Search WWH ::

Custom Search