Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
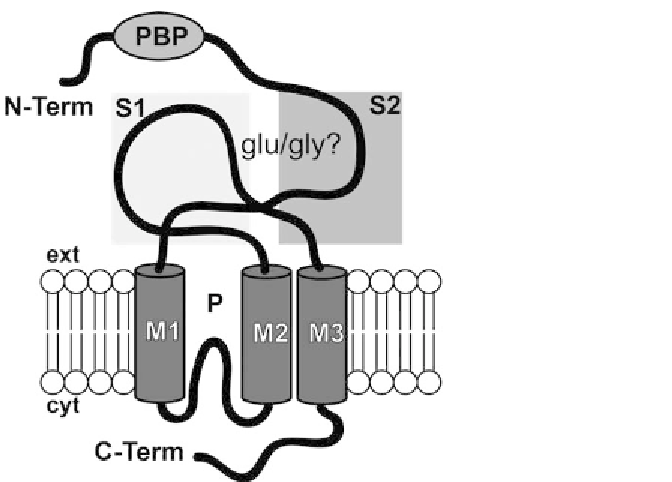
Fig. 13.1.
Arabidopsis thaliana
glutamate-like receptors (
At
GLRs) are predicted to share
the ionotropic glutamate receptor (iGluR) channel structure, with three transmembrane
domains (
M
1,
M
2,
M
3) and a
P
domain forming a membrane-embedded pore loop when
subunits combine into a functional tetramer (Colquhoun and Sivilotti 2004).
At
GLRs also
share with iGluRs a similar putative ligand-binding motif formed by the interactions of
the S1 and S2 domains. Most
At
GLRs sequence before the
S
1andafter
S
2, including M3,
which is absent in
Synechocystis
GluR0, show limited sequence similarity to iGluR (Chiu et
al. 2002). Both
At
GLR and iGluR have long N-terminal domains (N-term) with similarity
to bacterial periplasmic binding proteins (PBP); the role of the N-terminus is not clearly
defined but it is thought to be involved in targeting, translocation and degradation (Kato et
al. 2005). P is confusingly sometimes referred to as M2; therefore, M2 and M3 domains are
then named M3 and M4, respectively; S1 and S2 have been called GlnH1 and GlnH2
In animals, iGluR subunits are generally non-selective cation channels
(NSCCs) that propagate impulses across vertebrate neuronal or invertebrate
neuromuscular junctions through glutamate-gated Na
+
and/or Ca
2+
entry
(Dingledene et al. 1999). iGluR subunits can be grouped into seven subfam-
ilies according to primary amino acid sequence which have been further
classifiedintofourreceptorfamiliesaccordingtotheirsensitivitytospecific
amino acids and electrophysiological as well as pharmacological proper-
ties [GluR
α
α
(GluR1-4);
-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propi-
β
γ
δ
onic acid, AMPA], [GluR
(GluR5-7), GluR
(KA1,2); kainate], [GluR
δ
ε
ζ
χ
(
(NR3A,B);
N
-
methyl-D-aspartate, NMDA] (Hollmann and Heinemann 1994; Sprengel
1,2); orphan], [GluR
(NR2A-D), GluR
(NR1), GluR
Search WWH ::

Custom Search