Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
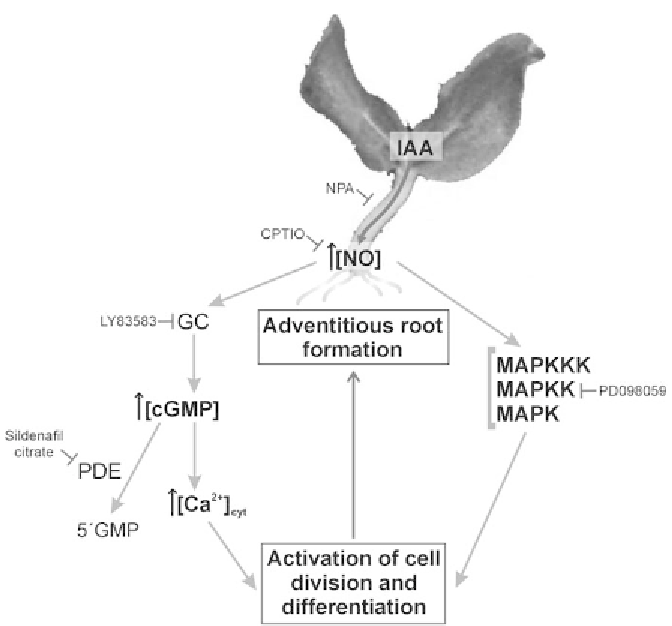
Fig. 9.3.
Schematic representation that integrates the signaling pathways and molecules
involved in the indole acetic acid (
IAA
) - and the NO-induced adventitious root formation
(
ARF
) in cucumber explants. The auxin IAA is synthesized in the shoot apical meristem of
the seedling and is basipetally transported to the basal region of the hypocotyl. There, IAA
triggers a local and transient generation of NO in a yet unknown manner (Pagnussat
et al. 2002). Thereafter, an NO-mediated cyclic GMP (
cGMP
)dependentpathwaythat
probably includes the modulation of cytosolic Ca
2+
concentration is operative to trigger
ARF (Pagnussat et al. 2003; Lanteri et al., submitted). In parallel, a cGMP-independent
pathway that involves the activation of a mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascade
is required for ARF (Pagnussat et al. 2004). Both pathways could mediate downstream
responses including the induction of cell division and differentiation resulting in ARF.
NPA
1-naphthylphthalamic acid,
GC
guanylate cyclase,
PDE
phosphodiesterase,
⊥
inhibition
Overall, the available data suggest a picture in which basipetal transport
of auxins induces an NO burst in the basal region of the hypocotyl, where
the adventitious root primordia develop. Then, NO triggers a bifurcated
signaling cascade that includes both cGMP-dependent and -independent
pathways. The activation of both pathways seems to be required for ARF
Search WWH ::

Custom Search