Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Dry
Wet
1
1
0.8
0.8
0.6
0.6
0.4
0.4
0.2
0.2
0
0
0
100
200
300
400
500
0
100
200
300
400
500
Soft
1
1
0.8
0.8
0.6
0.6
0.4
0.4
0.2
0.2
0
0
0
100
200
300
400
500
0
100
200
300
400
500
Med
1
1
0.8
0.8
0.6
0.6
0.4
0.4
0.2
0.2
0
0
0
100
200
300
400
500
0
100
200
300
400
500
Hard
Image Number
Image Number
Figure 3.27
Estimation of rock composition for the simulated on-line conveyor belt application.
Dots: model predictions. Solid lines: true weight compositions. Columns: dry and wet rocks. Rows:
soft, medium and hard rocks, from top to bottom. From Tessier
et al.
[26]
rocks occur for images in the range 350-400. For wet rocks, specular reflection due
to wet surfaces seems to be confounded with the shiny surface of MS rocks. This
may explain why MS composition (soft rocks) is overestimated by 20-30% in the
first half of the test. This problem is less important in the second half of the test
where either 100% or 0% MS is present on the conveyor. Adding imaging hardware
to remove specular reflection combined with contrast enhancement methods may
help improve classification results for wet rock mixtures. Since this was one of the
first attempt to directly take into account surface moisture in the rock type classifica-






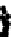





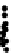












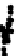



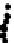













































































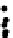


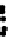








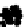



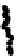












































































































































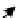







































































































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search