Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
3.5 Analysis result
1. Analysis of each area
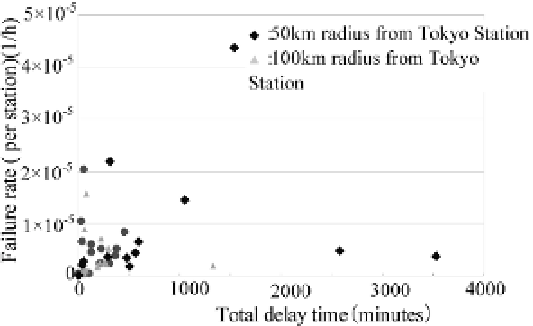
We analyzed the data of signalling operation malfunctions in each area.
Consequently, it becomes clear that the impact on customers is greater
in an area within a 50 km radius of Tokyo (see fig.4). Up to now, we
have concentrated on improving more trouble-free equipment in the 100
km radius around Tokyo Station, but have realized that it is more cost-
effective to bring the radius down to 50 km, and that a greater number
of passengers enjoy the benefits.
Fig. 4. Analysis in each area
2. Analysis of cause of system downs within 50 km radius from Tokyo.
It is clear that there is more serious impact within a 50 km radius
from Tokyo Station than in other areas. Failure related to cables and
CTC/PRC has greater effect on customers but the probability of occur-
rence is low. In addition, electronic interlocking systems have a higher
probability of breaking down, as well as having a greater impact on cus-
tomers.
(a) CTC/PRC system down.
Failure causes of CTC/PRC are analyzed and the frequency of soft-
ware bags is greater.
(b) Cable breakdown.
For cables, “man-caused failure” such as wiring mistakes related to
construction is the main cause of breakdowns. “Design and manufac-
ture” is mistakes in connecting.
(c) Electronic interlocking system.
For electronic interlocking systems, “constant failure” has a higher
occurrence, such as transitory communication abnormalities.
Main measures policy. Based on these analyses, we examined which stage
of RAMS is appropriate to return to when measures are taken.