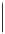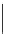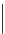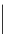Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Tabl e 7 . Proposed risk table
ID
HR SIL equivalent
10
−
9
/h
E
4
10
−
8
/h
D
3
3
·
10
−
7
/h
C
2
10
−
5
/h
B
1
10
−
5
/h
A
>
n. a.
so that a train may run over points which are set in an incorrect direction.
If passenger trains at high speed ran over these points, then ID E would be
determined from Table 5 leading to a THR of
10
−
9
per operating hour per
set of points.
In another example, =LGF from Table 2, the main hazard would be that
road trac would not be protected by the level crossing and the consequence
might be a collision at the level crossing, from which ID D would derive from
Table 5 leading to a THR of
10
−
8
per operating hour per level crossing. Note
that usually these THRs are reduced by risk reduction factors or mitigation
barriers, so that normally the THRs derived from the risk matrix are not the
THRs for the technical functions.
For accident types not classified in Table 5, either classification could be done
by analogy or statistical data or expert judgement could be applied directly.
For example, if it were judged that a particular accident typically results in
a single fatality, then ID D would be chosen based on Table 4. If statistical
evaluation resulted in a FWI value of 0.05 with 90% confidence, then the ID
C should be chosen from Table 4.
8
Conclusions and Outlook
The risk acceptance and setting of THR for technical systems could be based
on a risk matrix as explained in this document. In a next step, it is possible
to take a set of typical barriers into account. Some examples of how to fulfil
RAC-TS with the risk matrix are given in this document.
When using the risk matrix, mutual recognition will also depend on the list
of functions to which the risk matrix is applied. So, the use of a common
risk matrix will facilitate the mutual recognition process, but not lead to an
automatic approval.
References
1. Braband, J. (2005). Risikoanalysen in der Eisenbahn-Automatisierung, Tet-
zlaff, 2005
2. Braband, J. (2007): A proposal for common safety methods for risk assess-
ment in European Railways, Signal&Draht, 4/2007, 34-37