Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
NFQ
R
R
NFQ
R
(a)
(b)
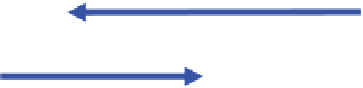
Figure 4.9
(a) The TaqMan
quantification system consists of two PCR primers and an internal
probe that hybridizes within the amplified region; (b) as the primer extends it encounters the
probe, the 5' exonuclease activity of the
Taq
polymerase degrades the probe: the reporter molecule
is no longer in proximity to the quencher and fluoresces
of PCR products as they are generated - real time. This was first developed using
ethidium bromide: as PCR products are generated in each cycle, more ethidium
bromide intercalates with the double-stranded DNA molecule and fluoresces under
UV light. The increase in fluorescence can be detected using a suitable 'camera' [49].
Increasingly sensitive assays have been developed, such as SYBR
Green and the
TaqMan
system. Using SYBR
Green, as PCR products are generated, the dye
binds to the double-stranded product and the fluorescence increases. The TaqMan
system uses a different approach, with two primers and a probe; the probe is within
the region defined by the primers and is labelled on the 5
end with a fluorescent
molecule and on the 3
end with a molecule that quenches the fluorescence. As
the primers are extended by the
Ta q
polymerase, one of them meets the probe,
which is degraded by the polymerase, releasing the probe and the quencher into
solution - efficient quenching of the fluorescent molecules only occurs when they
are in close proximity on the probe molecule (Figure 4.9).
As more PCR products are generated, more fluorescent molecules are released
and the fluorescence from the sample increases (Figure 4.10). Real-time assays are
highly sensitive, human specific and are not labour intensive. In addition to detecting
the quantity of DNA they have also been designed to detect PCR inhibition, DNA
degradation, male-specific DNA (Y chromosome) and mitochondrial DNA [50 - 61].
DNAIQsystem
A novel approach to quantification is used in the commercially available DNA IQ
Isolation System (Promega Corporation). The isolation method is based on salting-
out and binding to silica: a very specific amount of silica-coated beads is added to
the extraction and these bind a maximum amount of DNA; therefore, when the DNA
is eluted from the beads the maximum concentration is known. It has the advantage
of combining the extraction and quantification steps and can be semi-automated, but
has the disadvantage of not being human specific.