Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Add FTA
Purification reagent-
incubate at RT
Add TE-
incubate at RT
Remove TE
Allow discs
to dry
Replace FTA
Purification reagent
Replace TE
Repeat 2-3 times
Repeat 2-3 times
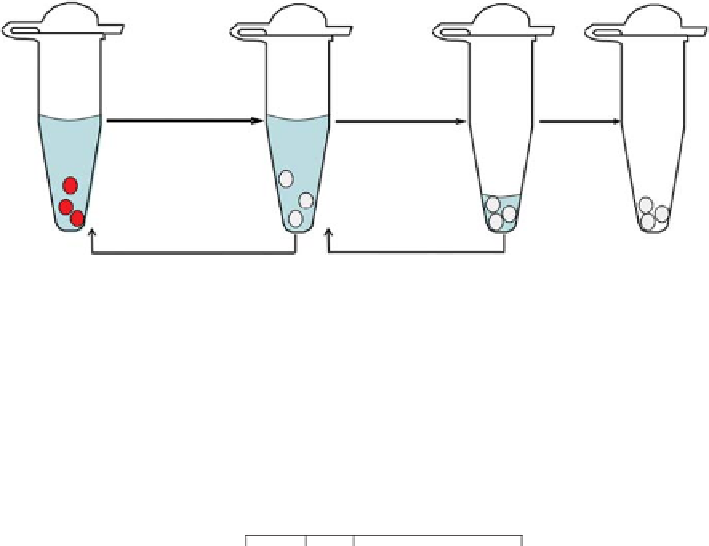
Figure 4.4
DNA extraction from blood on FTA
paper. (a) Sections of the FTA
card are removed
with a punch (usually 1.2 mm or 2 mm diameter), added to FTA
purification reagent, mixed and
incubated at room temperature for 5 minutes; one or more punched discs can be added to the
extraction. (b) The liquid is removed and replaced with fresh purification reagent; this process
is repeated two or three times. (c) The discs are then washed two or three times in TE (10 mm
Tris-HCl, 0.1 mm EDTA, pH 8.0). (d) Finally, the TE is removed and the FTA
discs, containing the
DNA, are left to dry at room temperature or with gentle heat (approximately 50
◦
C). The discs can
now be added directly to a PCR reaction
head
midshaft
tail
nucleus
acrosome
mitochondria
Figure 4.5
The nucleus in the spermatozoa is protected by the acrosome
is capped by the protective acrosome, which is rich in the amino acid cysteine; a
large number of disulfide bridges form between the cysteine residues in the acro-
some. Proteinase K, which is a general proteinase, cannot break the disulfide bonds:
however, the addition of dithiothreitol (DTT), a reducing agent that will break the
disulfide bonds, greatly increases the release of spermatozoa DNA [20].
Another complication with semen is that it is often recovered as a mixture of
spermatozoa and epithelial cells. The acrosome can be an advantage in these cases
as it is possible to perform differential lysis: the epithelial cells are broken down
by mild lysis conditions and the spermatozoa can be effectively separated from the
lysed epithelial cells [20, 21].
Hair shafts
Hair shafts that have been pulled out often possess a root that is rich in cellular mate-
rial and DNA can be extracted using any of the commonly used techniques - plucked