Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
a
b
Foliar and fine root litter
oody litter
Foliar and fine root litter
Woody litter
MP
HCP
LCP
L
WP
L
MP
HCP
LCP
L
WP
L
CO
2
CO
2
CO
2
CO
2
Inorganic
N
Microbial
biomass
CO
2
CO
2
CO
2
Microbial
biomass
Inorganic flows
CO
2
Mineralisation
Immobilisation
S
m
CO
2
Young
SOM
Young
SOM
S
y
Organic flow
Stabilisation/
humification
Old
SOM
Old
SOM
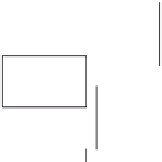
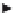
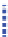
Fig. 4.4
Pools and fluxes of (
a
) carbon and (
b
) nitrogen in the new decomposition model. MP:
metabolic pool; HCP: holocellulosic pool; LCP: ligno-cellulosic pool; L: lignin; SOM: soil
organic matter; Sm: stabilisation coefficient for microbial biomass; Sy: stabilisation coefficient for
young SOM (From Corbeels et al.
2005)
SOM into more recalcitrant forms (respectively into young and old SOM). Nitrogen
is mineralized to, or immobilized from, the soil inorganic N pool to maintain the
N:C ratio of decomposing microbial biomass within a specified range. Balancing
potential microbial N demand against inorganic N availability determines whether
the activity of decomposers is limited by N. If so, then simulated decomposition
fluxes are reduced. The maximum rate of microbial N uptake is proportional to
soil inorganic N content. Lignin incorporation in the young SOM pool results in
additional N immobilization in the young SOM pool, which simulates the process
of chemical N immobilization.
SoilErosion: Water Runoff and Soil Erosion by Water
The runoff-erosion component was developed by UNIMI. It simulates surface
runoff and erosion, and handles irrigation events. The same soil description as in
the SoilW component can be used. Runoff and erosion can be simulated daily when
only daily rainfall is available, or for shorter time periods, if hourly or more
frequent data are available. The following four processes are simulated, allowing
for easy interchangeability and extension of options:
•
Interception of rain by vegetation; two approaches (von Hoyningen-Huene
1981
; Brisson et al.
1988)
are available, both of which calculate interception as
a function of Leaf Area Index.
Interception of rain by mulch.
•
•
Runoff using either the Curve Number approach, which is suitable for daily rain
data (SCS
1972)
or the kinematic wave approach, when hourly or more detailed