Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
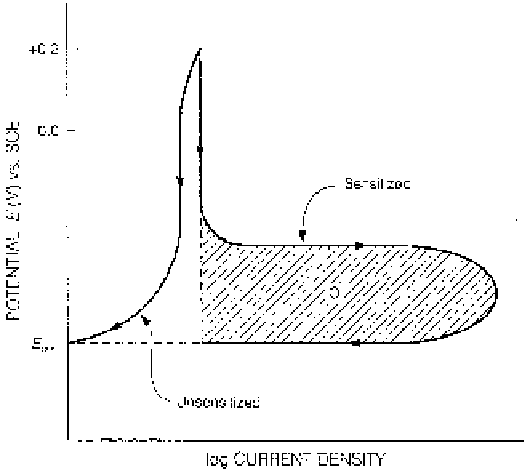
Figure 3.21
Schematic representation of procedure for electrochemical potentioki-
netic reactivation (EPR) study to determine sensitization.
denum carbide causes molybdenum depletion and susceptibility to intergranular
attack in hot reducing acids as well as in HNO
3
. Reduction of carbon and silicon
has imparted improved resistance. Hastelloy B and C become susceptible when
heated in the range of 500-705
C in which immunity can be restored by suitable
heat treatment at higher temperatures (1150-1240
°
C).
Copper alloy 260 (70-30 brass) corrodes intergranularly in dilute aqueous
solutions of H
2
SO
4
,Fe
2
(SO
4
), BiCl
3
, and other electrolytes. Enrichment of grain
boundary region in zinc through segregation is considered to be the cause of
attack.
Segregated iron at the grain boundary makes the high-purity aluminum suscep-
tible to intergranular corrosion. The precipitated phases in the high-strength
alloys are the cause for intergranular attack. For example, CuAl
2
precipitation in
Duralumin-type alloys causes copper depletion and a substantial potential differ-
ence is set up between the depleted area and the adjacent material. In 5000 and
7000 series alloys, precipitated phases like FeAl
3
,Mg
5
Al
8
, MgZn
2
, etc., at the
grain boundary are anodic with respect to the grain matrix. Solution heat treat-
ment eliminates the susceptibility to intergranular corrosion at the cost of loss
in strength. Attack along the boundaries of grains elongated in the rolling direc-
°