Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
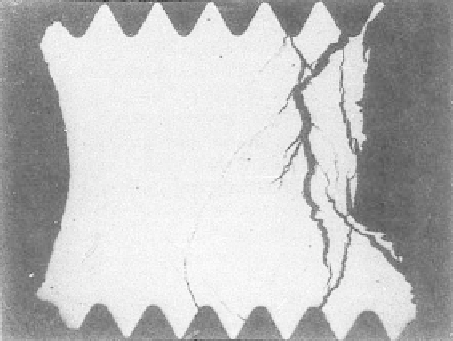
Figure 8.17
Longitudinal section of a 4137 steel bolt failed by HSC showing crack
emerging from thread grooves [21].
showed extensive corrosion deposits. The failed bolts were replaced with 17-4
PH stainless steel having a hardness of 22 HRC.
Collapse of the Point Pleasant, West Virginia (USA) bridge began by failure
of a 1060 steel eyebar [18]. Sulfur compounds were found on the fracture surface
and are believed to have caused hydrogen sulfide cracking in the eyebar.
An example of hydrogen attack is provided by the failure of a steel pipe
(0.22% C), 0.31% Si) used as a hot-gas bypass line for hydrogen-rich gas at 34
MPa and 320
C [22]. After 15 months of service, the pipe ruptured, causing a
serious fire. The microstructure showed interconnected grain boundary fissures
and radially aligned voids as a result of internal methane formation.
°
8.6 PREVENTIVE METHODS
Hydrogen blistering
may be prevented by the applications of one or more of the
following measures:
1.
Control of inclusions in steel
. Since inclusions play a big role in blistering
or flaking, inclusion-free ''clean'' steels are recommended. Elongated inclu-
sions are particularly detrimental, as their presence induces delamination.
Use of low-sulfur, calcium-treated, argon-blown steels reduces the incidence
of hydrogen blistering, as the poisoning effect of sulfur or sulfides on hydro-
gen evolution is reduced at low sulfur levels. Also, a treatment with synthetic
slag or the addition or rare earth metals can favor the formation of less detri-