Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
7.2.2 Factors Influencing LME
Effect of Grain Size
The yield stress and the fracture stress of a metallic material normally bear a
linear relationship with the inverse square root of grain diameter, which is known
as the Hall-Petch relationship:
σ
σ
1
kd
1/2
where
σ
yield stress or fracture stress
d
grain diameter
constants
The same relationship holds true for LME as well. A linear decrease of fracture
strength as a function of
d
1/2
, where
d
is the average grain diameter, has been
observed for copper and iron in molten lithium, 70-30 brass in mercury, and
zinc in mercury, indicating that coarser grained materials are more susceptible
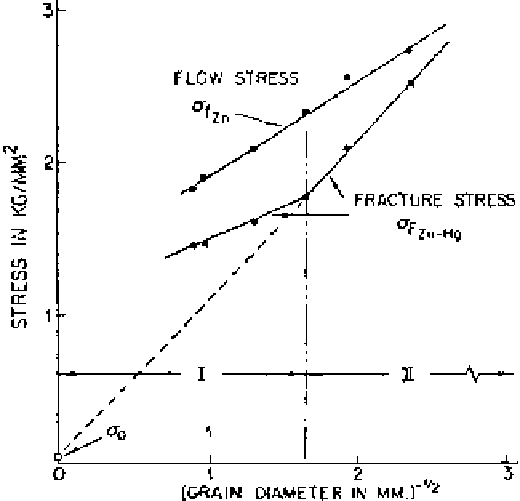
to LME. Figure 7.6 shows the variation of flow and fracture stresses of amalgam-
d
i
,
k
Figure 7.6
Variation of flow and fracture stresses of amalgamated zinc specimens
with grain size at 25
°
C [8].