Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
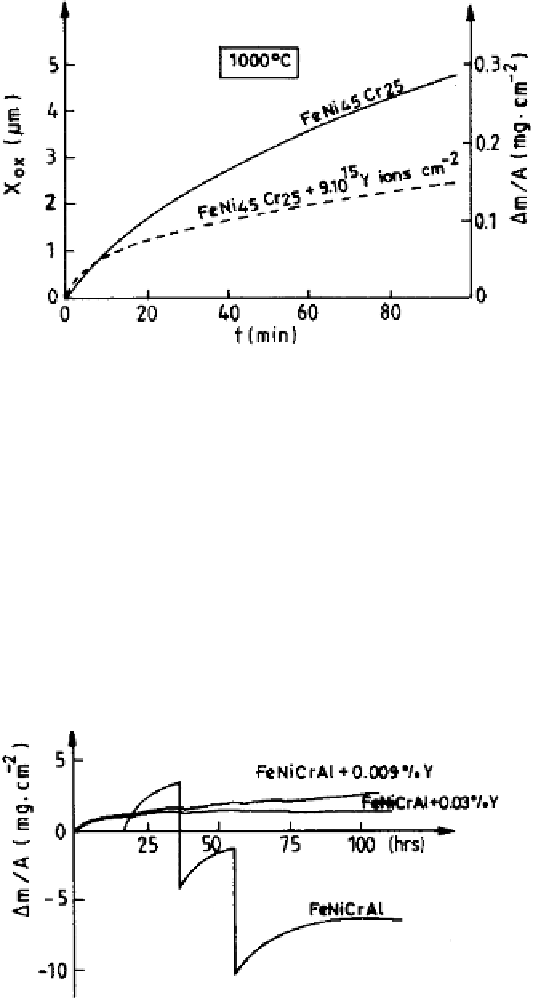
Figure 6.20
Isothermal oxydation of FeNiCr alloy with and without reactive element
[39].
the dominant transport mechanism in the presence of a reactive metal oxide
dispersion.
4.
The transient oxidation stage is shortened and less base metal oxidation occurs.
5.
Void formation/accumulation at the alloy-Al
2
O
3
or alloy-Cr
2
O
3
interface
is reduced.
6.
The adherence of the scale to the alloy substrate is substantially increased
in both the types of alloys.
7.
The integrity of the oxide scales is improved.
Figure 6.21
Oxidation of FeNiCrAl alloy with and without reactive element under
thermal cycles [39].