Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
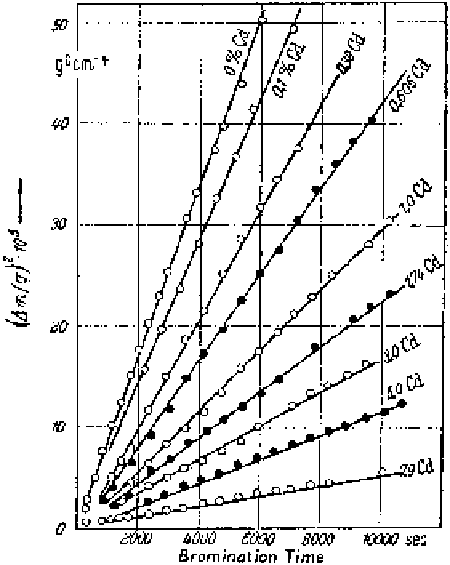
Figure 6.3
Parabolic course of the weight increase during the bromination of silver
and silver-cadmium alloys at 330°C and 170 mm Hg bromine partial pressure, according
to Hauffe and Gensch (∆
m/q
in g/cm
2
; the numbers on the straight lines denote at.% Cd).
6.3 INTERNAL OXIDATION AND CATASTROPHIC
OXIDATION
6.3.1 Internal Oxidation
Internal oxidation is a process whereby oxygen diffuses into an alloy and causes
subsurface precipitation of the oxides of one or more alloying elements. This
subject has been well reviewed by Rapp [9], Swisher [10], and Meijering [11].
It is already known that at high temperatures there exists a possibility for dissolu-
tion of nonmetallic species, such as O, C, and S, into metals and alloys. The
dissolution and diffusion of oxidants into the alloys introduces some embrittle-
ment and causes subsurface precipitation of oxides, carbides, or sulfides of the
more reactive components in the alloys. Dilute solid solution alloys comprising
such base metals as Fe, Ni, Co, Cu, and Ag, with less noble alloying elements