Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
highest concentration exists in the oxide in equilibrium with the metal and is
insensitive to the partial pressure of oxygen in the external environment. Then
either of the concentration terms, i.e.,
C
I
or
C
II
, may be given by:
C
II
P
1/6
ext
and
C
I
P
1/6
*
where
P
ext
dissociation
pressure of the oxide in contact with Zr. Therefore, by expressing vacancy con-
centration in terms of local oxygen partial pressure, Eq. 5.118 can be transformed
into:
pressure of the oxidant at the scale-gas interface,
P
*
kT
P
*
P
ext
σ
H
1)
ln
(5.119)
6
Ω
M
(
φ
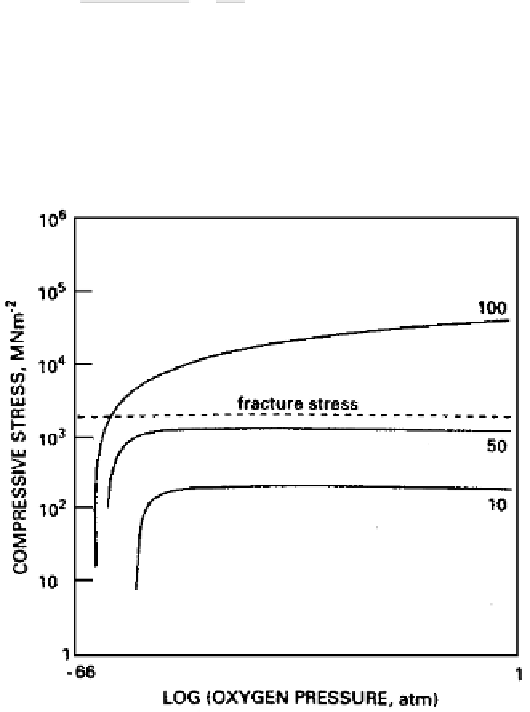
This equation is plotted in the form of compressive stress vs. log oxygen pressure
and depicted in Fig. 5.26 for the case of zirconia (the line marked ''100''). The
calculations have been performed using values of
φ
1.56,
Ω
M
10
29
m
3
, and
a ZrO
2
dissociation pressure of
P
*
8
10
68
atm at 773 K. This figure also
Figure 5.26
Stress-induced reductions in oxidation rate for an oxide (zirconia) grow-
ing by anion diffusion at 773K. Numbers on curves give percentage drop in oxidation
rate under stress [Ref. 51].