Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
more than required for complete protection, the situation is described as overpro-
tection. An overprotected steel structure will still be protected, but this will mean
an unnecessary wastage of current. The risk of stray current corrosion (Section
4.4.3) of the neighboring metallic structure also enhances with the excess current.
For amphoteric metals like zinc and aluminum, overprotection increases corro-
sion because of the excess alkalis generated at the metal surface. Such a situation
is sometimes referred to as
cathodic corrosion
.
4.4.2 Methods of Application
There are two methods for the application of cathodic protection:
1.
Use of a sacrificial anode, and
2.
Use of an impressed current
Sacrificial Anode System
The action of sacrificial anodes has been discussed in Section 3.3.3. A less noble
metal in galvanic contact with another metal higher up in the emf series behaves
as an anode member in the couple and sacrifices its life to protect the nobler
metal, which acts as a cathode. All that is required is to provide galvanic coupling
between the two metals. This may be achieved by direct contact, as in a coating,
e.g., galvanizing, or by electrical contact through a conducting wire. Magnesium,
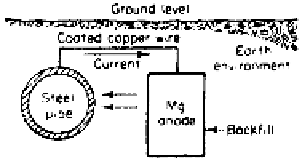
zinc, and aluminum are used to protect steel. The schematic diagram for the
protection of a buried pipeline by use of sacrificial anode is shown in Fig. 4.10.
For protection of the inner wall of a pipe or tank the anode is to be suitably held
inside and connected electrically with the wall.
To act as a sacrificial anode a metal should fulfill the following requirements:
1.
The potential difference between the anode and the corroding structure must
be large enough to overcome the local cells on the corroding metal.
2.
The anode material must have sufficient electrical energy content to last for
a reasonably long period before replacement. The electrical energy content
is expressed by the term ''ampere-hour per pound'' (or ''kg''), meaning
Figure 4.10
Schematic representation of cathodic protection by sacrificial anode.