Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
particular the data can be displayed; it has a size specified as a number of rows and
columns. Further discussion is provided in Sect.
7.8
.
This type of virtualisation is common in many other, non-preservation related,
areas. It is the basis on which computer operating systems can work, surviving
many generations of changes in component technologies, on a variety of hardware.
For example, the operations which a disk drive must perform can be specified and
used throughout the rest of the operating system, but the specifics of how that is
implemented are isolated within a driver library and drive electronics. The under-
lying idea here is, in software terms, to define a set of interfaces which can be
implemented on top of a variety of specific instances which will change over time.
7.2 Overview of Techniques for Describing Digital Objects
The OAIS Reference Model standard has a great deal to say about Information
Modelling in general terms and a number of these ideas are used in this section.
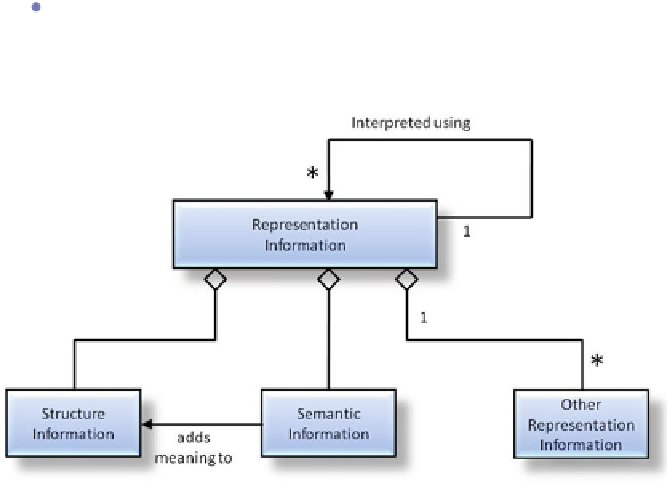
Figure
7.1
shows Representation Information can contain Structure Semantic and
Other Information. In the following sub-sections we describe some of the basic
techniques for each of these types and then give some examples of applying these
to the various classifications of digital objects presented in
Chap. 4
.
It is important to note that the classification indicated in Fig.
7.1
does not require that the various pieces are separate digital objects,
or separate digital files. For example a single document could pro-
vide all these types of Representation Information, possibly heavily
intertwined.
Fig. 7.1
Representation information object