Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
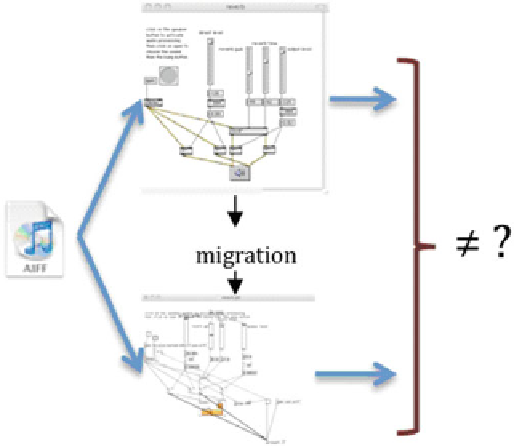
Fig. 22.8
Checking authenticity
Multimedia Performances (IMP) [
221
]. The section describes several different IMP
systems and presents an archival system, which has been designed and implemented
based on the CASPAR framework and components for preserving Interactive
Multimedia Performances.
22.5.1 Introduction
IMP is chosen as part of the testbeds for its challenges due to the complexity and
multiple dependencies and typically involves several difference categories of digital
media data. Generally, an IMP involves one or more performers who interact with a
computer based multimedia system making use of multimedia contents that may be
prepared as well as generated in real-time including music, audio, video, animation,
graphics, and many others [
222
,
223
].
The interactions between the performer(s) and the multimedia system [
224
-
226
]
can be done in a wide range of different approaches, such as body motions (for
example, see Music via Motion (MvM) [
227
,
228
]), movements of traditional musi-
cal instruments or other interfaces, sounds generated by these instruments, tension
of body muscle using bio-feedback [
229
], heart beats, sensors systems, and many
others. These “signals” from performers are captured and processed by multimedia
systems. Depending on specific performances, the input can be mapped onto mul-
timedia contents and/or as control parameters to generate live contents/feedback
using a mapping strategy.