Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
most plants, although some plants prefer one
end of the range to another. Ericaceous plants
like blueberries, rhododendrons and azaleas
prefer a pH at or below pH6 where iron is
freely available. Brassicas (cabbage, broccoli)
and beans are best at pH 7.5 to pH 8 where
there is plenty of calcium. Most plants,
however, can grow in a wide range of pH levels.
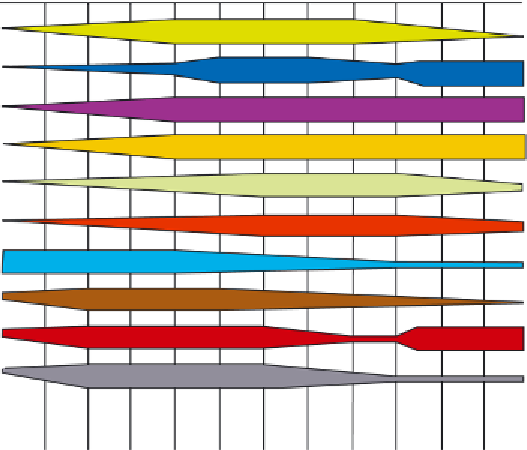
The pH of the soil influences the availability
of nutrients to the plant (see Figure 1.11).
Plants grow only as fast as the least available
nutrient; that is, if all nutrients are available
to the plant except, for example, iron as it is
an alkaline soil, the lack of this one element
will retard the growth of the plant in general.
The range of pH 6 to pH 7.5 ensures
maximum nutrient availability.
Figure 1.12
pH testing kits are freely available and easy
to use. The soil on the left
is alkaline (pH 9). The soil on
the right
is acid to neutral (pH 6).
A pH test is easy to perform (see Figure 1.12)
and can quickly solve the mystery of why a
certain plant is not thriving in the existing
Acid
Alkaline
4.0
4.5
5.0
5.5
6.0
6.5
7.0
7.5
8.0 8.5
9.0
9.5 10.0
NITROGEN
PHOSPHORUS
POTASSIUM
SULFUR
CALCIUM
MAGNESIUM
IRON
MANGANESE
BORON
COPPER and ZINC
MOLYBDENUM
4.0
4.5
5.0
5.5
6.0
6.5
7.0
7.5
8.0 8.5
9.0
9.5 10.0
pH
Figure 1.11
Soil pH determines how available nutrients are to the plant. The wider the band the more available the
nutrient. (After K Handreck and N Black
Growingmediaforornamentalplantsandturf
)