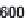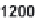Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 2.4
Differences in introduction frequency among reptile and amphibian taxa, excluding the
turtle
Trachemys scripta
. Solid bars are data for all introductions, open bars for successfully estab-
lished introductions, with establishment counted only once per jurisdiction
Fig. 2.5
Differential establishment success among introduced reptile and amphibian taxa, with
Trachemys scripta
included in the calculation for turtles
having more than ten introductions provides a better fit to data (Fig. 2.7).
Unsurprisingly, ability to successfully establish populations varies among families,
and those families having the greatest numbers of introductions are typically also
among those having the greatest numbers of naturalized populations (Table 2.3).
Certain artifacts characterize some of these results. First, families introduced fewer
times are more prone to estimation error; those introduced fewer than ten times are
distinguished in Table 2.3. Second, some of those families showing highest success
rates do so for unique reasons that do not make them representative. As one example,