Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
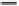
Food insecurity
Poverty
Change in priorities
for households
Health care utilization
Intake
Economic crisis
Local food prices
Food production
(auto-consumption)
Expenditure on education
Psychological well-being
Environmental
change and
agricultural
vulnerability
Variable global
commodity prices
(food, fuel, inputs)
Changes in
nutrition outcomes
Land cover
change
Seasonality and
rainfall
Short term
Climate variability
and
anthropogenic drivers
Negative
economic growth
rate
Stunting
Wasting
Infant birth weights
Morbidity
Long term
Poor cognitive
development
Adaptation to
changes in resources
Mortality
FIGURE 2.2
Conceptual framework that links climate variability and anthropogenic drivers to their consequences on food production to food prices
(source: derived from Darnton-Hill and Cogill, 2009; Woldetsadik, 2011).
Note
Light grey boxes are observable environmental parameters, mid-grey boxes are household-level factors, grey boxes are individual factors and dark grey boxes are societal
factors.































Search WWH ::

Custom Search