Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
OCH
2
COOH
OCH
2
COOH
OH
Cl
Cl
Cl
OH
Cl
Cl
Cl
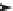
2,4-D
O
OH
OH
COOH
HOOC
C
HOOC
Cl
Cl
OH
OH
Cl
O
Cl
Cl
Cl
O
COOH
COOH
COOH
HOOC
COOH
COOH
COOH
C
Cl
COOH
CH
2
CH
2
COOH
Succinic acid
O
Cl
O
O
Herbicides such as monuron, diuron, linuron, and propanil are metabolized through
catechol intermediates. Endosulfan undergoes degradation with the help of mycobacte-
rium and forms endosulfan diol and endosulfan lactone.
3.4.4 Carbamate Pesticides
Carbamate pesticides are transformed metabolically by a variety of chemical reactions
into more water-soluble molecules with increased polar properties. The principal route of
metabolism of carbamate esters is
1.
via oxidation
: Generally associated with the mixed-function oxidase enzymes.
Depending on the functional groups in the molecules, oxidative reactions include
(a) hydroxylation of aromatic ring, or epoxidation, (b) O-dealkylation, (c) N-methyl
hydroxylation, (d) N-dealkylation, (e) hydroxylation and subsequent oxidation of
aliphatic side chain, and (f) thio ether oxidation to sulfoxides and sulfones.
2.
via hydrolysis
: Carbamates are hydrolyzed by esterases to form amine, CO
2
, alco-
hol, or phenol.
3. via conversion of conjugated compounds to hydroxy products.
Aldicarb, methomyl, and oxamyl on hydrolytic metabolism form pesticide oxime as a
major product, which is then degraded to carbon dioxide in soil.
Propham and chlorpropham undergo hydroxylation at position 2 and 3. Oxidation and hydro-
lysis form 1, 3 hydroxy and 1-carboxy derivates, which are converted into hydroxy acetanilide.
Phenmedipham and desmedipham are hydrolyzed mainly into methyl-N or ethyl-N-(3-
hydroxy phenyl carbamate), which are hydrolyzed to 3-amino phenol.
Carbaryl undergoes hydroxylation and hydrolysis in the presence of microbes to form
1-Naphthyl N-hydroxy methyl carbamate (due to the hydroxylation), 4-Hydroxy-1-naphthyl-
N-methyl carbamate, 5-Hydroxy-1-naphthyl-N-methyl carbamate, and 1-Naphthol via


































Search WWH ::

Custom Search