Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
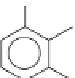
Carbofuran
: The photodegradation of broad-spectrum insecticide of N-methyl car-
bamate ester series does not occur predominantly, but when it occurs, it undergoes
hydrolysis, oxidation, and methyl and photo-Fries rearrangements to form a number of
products as
O
CH
3
C
O
O
NH
O
O
O
h
ν
H
2
O
C
+
CH
3
NH
H
2
O
O
OH
O
h
ν
H
2
O
C
CH
3
OH
NH
Decompose
OH
OH
OH
OH
O
CH
3
NH
2
+ CO
2
H
2
O
N-methylcarbamates (Carbaryl or propoxur)
by UV irradiation undergo cleavage of the ester
bond, resulting in the production of the phenol or heterocyclic enol of the carbamate ester.
The rate of photolysis depends on the pH of the medium. Similar results were reported
for photodecomposition of other carbamate esters, for example, bendiocarb, pirimiphos-
methyl in aqueous solution, etc.
3.3.4 Pyrethroid Pesticides
Pyrethroid pesticides are the derivatives of chrysanthemic acid, containing an isobutenyl
group, and are very much susceptible to photochemical oxidation. Pyrethroid pesticides
undergo photolysis by hydrolysis of the ester bond, cis-trans isomerization, carboxylation,
and reductive dehalogenation.
Cypermethrin, deltamethrin, permethrin, and fenvalerate undergo photodegradation
by cleavage of the ester or diphenyl ether linkage, oxidation of the -C=O group to -COOH
group, hydration of the CN group, hydrolysis of CONH
2
group to -COOH group, oxidative
cleaving of the halogenated side chain, and dehalogenation and intramolecular cycliza-
tion to form γ or δ lactone. In distilled water, the photolysis was in the order deltame-
thrin > cypermethrin > permethrin > fenvalerate and t
1/2
ranged from 1.4 to 10 days. The
photodegradation rate on soil surface was correlated with the content of organic matter in
the soil.































Search WWH ::

Custom Search