Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
7. C-Oxidation
O
H
2
C
OH
H
2
C
H
3
C
1
O
2
O OH
O
H
2
C
O
O
O
3
H
3
C
H
3
C
H
3
C
R
H
3
C
R
H
3
C
R
H
3
C
R
O
R
O
3
O
2
R
HOOC
OHC
HOH
2
C
O
H
3
C
H
O
R
H
3
C
H
3
C
H
3
C
R
R
R
HO
H
3
C
R
8. S-Oxidation
S
O
O
O
OCH
3
OCH
3
S
CH
3
ArO
P
S
CH
3
ArO
P
S
CH
3
R
OCH
3
OCH
3
R
R
O
9. Rearrangement
S
O
OCH
3
OCH
3
(a)
ArO
P
ArO
P
OCH
3
SCH
3
R
1
H
R
1
H
NH
2
NH
2
R
1
R
1
R
2
N
R
2
N
or
(b)
R
2
R
2
O
O
O
O
10. Cyclization
CI
CI
CI
CI
NO
2
N
CI
(a)
(b)
CI
CI
CI
H
R
2
CI
H
N
N
H
H
R
2
R
1
CI
H
CI
CI
R
1
NO
2
NO
2
O
O
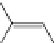
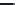
3.3.1 Photolysis of Organochlorine Pesticides
This class includes some of the well-known and popular compounds such as DDT, lin-
dane, chlordane, aldrin, endrin, endosulfan, chlorocamphene, etc. As these pesticides have
high persistence in environment, they pose a threat to the ecosystem.
Photochemically induced isomerization, dimerization, and dechlorination are common
reactions that occur in organochlorine compounds.
p,p
′
-DDT
: This popular insecticide, on photodegradation, produces the following com-
pounds by dechlorination, dimerization, and oxidation (Zayed et al. 1994).

































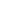
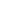

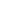

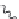
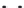



































Search WWH ::

Custom Search