Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
S
O
S
O
H
3
CO
H
3
CO
SH
CH
2
P
CH
2
P
S
N
S
H
3
CO
OH
H
3
CO
N
S
Hydrolysis
N
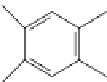
Methiodothion
N
OCH
3
OCH
3
Chlorpyrifos undergoes hydrolysis easily in alkaline medium (Gilani et al. 2010).
Cl
Cl
S
S
Cl
Cl
SC
2
H
5
SC
2
H
5
Alkaline
Hydrolysis
O
P
P
Cl
+ HO
N
SC
2
H
5
SC
2
H
5
OH
Cl
N
3.2.4 Carbamate Pesticides
Oxamyl and methomyl, widely used oxime pesticides, undergo rapid degradation in
anoxic and suboxic soil suspensions by a redox pathway involving Fe(II). During the
mechanism, Fe(II) forms a precursor complex that forms nitrile and thiol (Strathman and
Stone 2000).
R
O
O
Fe (II)
R
Fe (II) +
S
C= N
OC
NH
C = N
OC
NH CH
3
S
CH
3
CH
3
(Oxamyl or Methomyl)
CH
3
N
-
CH
3
NH
2
+ CH
3
NHCOO
-
R
C
CO
S CH
3
RC
N
+
CH
3
SH
N-Methylcarbamates undergo successive oxidation in soil and are converted to CO
2
as
the final product. Aldicarb or thiobencarb undergoes oxidative degradation easily in chlo-
rinated water.
During the studies on carbamate pesticides, the author himself found that the degrada-
tion of carbamate pesticides increased with soil organic matter, soil surface area, percent-
age clay content, temperature, and soil-moisture content (Bansal 2005), amending the soil
with farm yield manure (FYM). It was also found that degradation increased with pH and
was faster in alkaline medium (Bansal 2004).



































Search WWH ::

Custom Search