Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Degradation products
Parent compound
CH
2
CH
3
CH
2
CH
3
CH
2
CH
3
COCH
2
Cl
COCH
2
SO
3
H
COCOOH
N
N
N
CH
2
OCH
2
CH
3
CH
2
OCH
2
CH
3
CH
2
OCH
2
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
Acetochlor ESA
Acetochlor ethane sulfonic acid
Acetochlor OA
Acetochlor oxanilic acid
Acetochlor
CH
2
CH
3
CH
2
CH
3
CH
2
CH
3
COCH
2
Cl
COCH
2
SO
3
H
COCOOH
N
N
N
CH
2
OCH
3
CH
2
OCH
3
CH
2
OCH
3
CH
2
CH
3
CH
2
CH
3
CH
2
CH
3
Alachlor ESA
Alachlor ethane sulfonic acid
Alachlor OA
Alachlor oxanilic acid
Alachlor
CH
2
CH
3
CH
2
CH
3
COCH
2
Cl
COCH
2
OH
N
N
H
H
CH
2
CH
3
CH
2
CH
3
2-chloro-2',6'-diethylacetanilide
2-hydroxy-2',6'-diethylacetanilide
CH
3
CH
3
O
CH
3
H
3
C
N
CH
3
H
3
C
N
H
3
C
N
S
O
H
S
OH
S
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
Aldicarb oxime
Aldicarb nitrile
Aldicarb
CH
3
O
CH
3
O
O
H
3
C
N
CH
3
H
3
C
N
CH
3
S
H
S
H
O
O
CH
3
CH
3
O
O
Aldicarb sulfoxide
Aldicarb sulfone
CH
3
CH
3
O
N
N
H
3
C
H
3
C
S
O
OH
S
O
OH
CH
3
CH
3
Aldicarb sulfoxide oxime
Aldicarb sulfone oxime
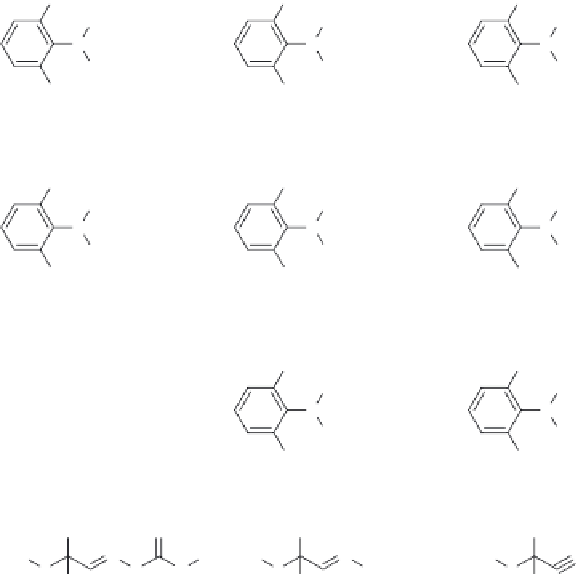
FIGURE 4.7
Chemical structures of pesticides and degradation products cited in
Table 4.1
.
with other degradation products of metribuzin; DK and DADK leached from the root zone
and were detected in 99% and 48%, respectively, of the groundwater samples analyzed
in average concentrations, considerably exceeding the EU limit value for drinking water
(0.1 μg/L). Both metabolites appear to be relatively stable and persisted in soil water and
groundwater several years after application. Groundwater contamination with metribuzin
metabolites has also been reported by Kjaer and coworkers (2002), based on the ground-
water samples from a sandy aquifer in Southern Denmark. While metribuzin and DA




























Search WWH ::

Custom Search